Refining the serum miR-371a-3p test for viable germ cell tumor detection
- PMID: 37386046
- PMCID: PMC10310745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-37271-1
Refining the serum miR-371a-3p test for viable germ cell tumor detection
Abstract
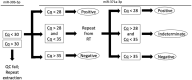
Circulating miR-371a-3p has excellent performance in the detection of viable (non-teratoma) germ cell tumor (GCT) pre-orchiectomy; however, its ability to detect occult disease is understudied. To refine the serum miR-371a-3p assay in the minimal residual disease setting we compared performance of raw (Cq) and normalized (∆Cq, RQ) values from prior assays, and validated interlaboratory concordance by aliquot swapping. Revised assay performance was determined in a cohort of 32 patients suspected of occult retroperitoneal disease. Assay superiority was determined by comparing resulting receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curves using the Delong method. Pairwise t-tests were used to test for interlaboratory concordance. Performance was comparable when thresholding based on raw Cq vs. normalized values. Interlaboratory concordance of miR-371a-3p was high, but reference genes miR-30b-5p and cel-miR-39-3p were discordant. Introduction of an indeterminate range of Cq 28-35 with a repeat run for any indeterminate improved assay accuracy from 0.84 to 0.92 in a group of patients suspected of occult GCT. We recommend that serum miR-371a-3p test protocols are updated to (a) utilize threshold-based approaches using raw Cq values, (b) continue to include an endogenous (e.g., miR-30b-5p) and exogenous non-human spike-in (e.g., cel-miR-39-3p) microRNA for quality control, and (c) to re-run any sample with an indeterminate result.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Refining the serum miR-371a-3p test for viable germ cell tumor detection: identification and definition of an indeterminate range.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 21:rs.3.rs-2644890. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2644890/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 29;13(1):10558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37271-1. PMID: 36993198 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ehrlich Y, Brames MJ, Beck SD, Foster RS, Einhorn LH. Long-term follow-up of Cisplatin combination chemotherapy in patients with disseminated nonseminomatous germ cell tumors: Is a postchemotherapy retroperitoneal lymph node dissection needed after complete remission? J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:531–536. doi: 10.1200/jco.2009.23.0714. - DOI - PubMed

