Comparison of oral candidiasis characteristics in head-and-neck cancer patients before and during radiotherapy
- PMID: 37388299
- PMCID: PMC10300268
Comparison of oral candidiasis characteristics in head-and-neck cancer patients before and during radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Patients undergoing head-and-neck radiotherapy are susceptible to Candida colonization and infection. This study aimed to identify oral Candida species type (ST), colony count (CC), and oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC) in head-and-neck cancer patients, undergoing radiotherapy, before and 2 weeks after radiation.
Materials and methods: In this quasi-experimental study, head-and-neck cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy (up to 6000 cGy) were recruited. Samples were taken before and 2 weeks after radiation therapy (RT). CC was assigned using Sabouraud dextrose agar culture medium and morphological studies were performed to confirm OPC. For identification, polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism was performed. Data were analyzed using Chi-square-test and kappa coefficient. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
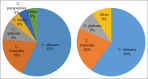
Results: Twenty-one of 33 patients were Candida positive. The detected fungal species included Candida albicans (60%), Candida tropicalis (22%), Candida glabrata (9%), and other species (9%). Following RT, OPC and CC changed significantly (P = 0.003 and P = 0.001, respectively), whereas ST did not significantly change (P = 0.081). Two new species (Candida krusei and Candida parapsilosis) were detected after the intervention. The OPC, CC, and ST changes after RT were not significantly related to malignancy site or radiation dose (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: The present study showed that OPC, CC, and ST were not related to the malignancy site. Following RT, OPC and CC changed significantly, while ST showed no significant change. The radiation dose and malignancy site had no effects on the OPC, CC, or ST alterations following RT.
Keywords: Candida; head-and-neck neoplasms; radiotherapy.
Copyright: © 2023 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Deng Z, Kiyuna A, Hasegawa M, Nakasone I, Hosokawa A, Suzuki M. Oral candidiasis in patients receiving radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;143:242–7. - PubMed
-
- Gligorov J, Bastit L, Gervais H, Henni M, Kahila W, Lepille D, et al. Prevalence and treatment management of oropharyngeal candidiasis in cancer patients: Results of the French CANDIDOSCOPE study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;80:532–9. - PubMed
-
- Schelenz S, Abdallah S, Gray G, Stubbings H, Gow I, Baker P, et al. Epidemiology of oral yeast colonization and infection in patients with hematological malignancies, head neck and solid tumors. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40:83–9. - PubMed
-
- Specht L. Oral complications in the head and neck radiation patient.Introduction and scope of the problem. Support Care Cancer. 2002;10:36–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources