Long-Term Outcomes of Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37388618
- PMCID: PMC10305785
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.39638
Long-Term Outcomes of Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review
Abstract
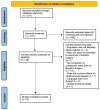
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is a minimally invasive procedure that usually takes two hours. It is commonly performed in refractory cases to help morbidly obese patients (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2) lose weight. It is well known that morbid obesity accompanies other comorbid conditions such as atherosclerotic diseases, strokes, cancers, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. It is crucial to treat this category of patients to improve their quality of life and minimize the chance of mortality in these patients. Given the importance of treating this group, we explored the long-term outcomes of patients who underwent bariatric surgery for cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and depression compared to those who did not. This systematic review utilized articles identified through PubMed using the following search terms: (morbidly obese OR obesity OR obese) AND (bariatric surgery OR metabolic surgery OR gastric bypass OR gastrectomy) AND (chronic disease OR chronic diseases OR cardiovascular diseases OR heart diseases OR cancer OR neoplasms OR stroke OR depressive disorder OR depression). The filter used was observational studies, which yielded 217 studies. Out of these results, eight citations were included in an observational study that met our eligibility criteria. From our search, the articles showed a clinically significant decrease in the incidence of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and depressive disorders after treatment with bariatric surgery. Furthermore, there was also a correlation between bariatric surgery and remission of type 2 diabetes. The surgery has an apparent protective effect on the development and progression of comorbid conditions accompanying morbid obesity. Overall, the quality of life has improved in patients who have undergone the procedure compared to those who have not. Bariatric surgery must be recommended as a beneficial option in managing morbidly obese patients (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2) who have responded poorly to first-line management plans.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; cancer; cardiovascular diseases; depression; gastric bypass; morbidly obese; roux-en-y gastric bypass.
Copyright © 2023, Raza et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bariatric surgery for people with diabetes and morbid obesity: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(22):1-23. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074527 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Bariatric Surgery Using Laparoscopic Banding, Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, or Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Usual Care Obesity Management With All-Cause Mortality.JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):279-290. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.20513. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 29340677 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss in Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SM-BOSS Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):255-265. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.20897. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 29340679 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative analysis of weight loss and resolution of comorbidities between laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 18 studies.Int J Surg. 2020 Apr;76:101-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.035. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32151750
-
Bariatric procedure selection in patients with type 2 diabetes: choice between Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020 Feb;16(2):332-339. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2019.11.013. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020. PMID: 31902579 Review.
Cited by
-
Continuous PPI Treatment After Gastric Bypass Increases the Risk of Pathological PTH Levels at 10 Years Postoperatively.Obes Surg. 2025 Mar;35(3):941-945. doi: 10.1007/s11695-025-07692-0. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Obes Surg. 2025. PMID: 39865206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Risk of heart failure in obese patients with and without bariatric surgery in Sweden—a registry-based study. Persson CE, Björck L, Lagergren J, Lappas G, Giang KW, Rosengren A. J Card Fail. 2017;23:530–537. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous