Clinical equivalence of Trusynth fast ® and Vicryl rapide ® polyglactin 910 fast absorbing sutures on maternal morbidity experienced by women following episiotomy repair: a single-blind, randomized study
- PMID: 37388624
- PMCID: PMC10300501
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.126555.2
Clinical equivalence of Trusynth fast ® and Vicryl rapide ® polyglactin 910 fast absorbing sutures on maternal morbidity experienced by women following episiotomy repair: a single-blind, randomized study
Abstract
Background: Episiotomy procedure enlarges the vaginal outlet to facilitate childbirth. Polyglactin 910 fast-absorbing sutures are widely used for the repair of episiotomy because of their rapid absorption and less inflammatory response. This study was designed for subjective assessment of perineal pain post-episiotomy repair, with Trusynth Fast ® and Vicryl Rapide ® polyglactin 910 fast-absorbing sutures. Method: This was a single-blind, randomized, prospective study conducted between January 7, 2021 and July 14, 2021 across two centers in India. Primiparous or multiparous women (18-40 years), who required episiotomy during vaginal delivery were included, and either Trusynth Fast ® (n=47) or Vicryl Rapide ® (n=49) suture was used for their episiotomy repair. The primary endpoint, perineal pain was assessed with visual analogue scale at all follow-up visits. The secondary endpoints, quantity of local anesthesia, number of sutures used, time to repair episiotomy, intraoperative suture handling, analgesics used, early and late wound complications, wound re-suturing, time to complete healing, presence of residual sutures, return to sexual activity, dyspareunia, and adverse events were also recorded. Results: The study showed no significant difference in perineal pain between the two groups at any visit. A statistically significant difference (p<0.05) in total score of episiotomy healing scale on day 2 (0.13±0.34 versus 0.35±0.56) and swelling on day 2 (8.51 versusversus 28.57%) was noted between Trusynth Fast ® and Vicryl Rapide ® group. Non-significant difference was observed between the groups regarding anesthesia, number of sutures, time to repair episiotomy, intraoperative suture handling, analgesics, puerperal fever, wound infection, dehiscence, hematoma, urinary incontinence, re-suturing, time to complete healing, return to sexual activity and dyspareunia. Conclusion: Trusynth Fast ® suture is clinically equivalent to Vicryl Rapide ® suture and can be used for episiotomy repair with minimal risk of perineal pain and wound complications. Clinical Trials Registry of India Registration: CTRI/2020/12/029925; Registered on December 18, 2020.
Keywords: Episiotomy healing scale; Episiotomy repair; Perineal pain; Polyglactin 910 fast absorbable suture; Vaginal delivery; Wound complications.
Copyright: © 2023 Hemalatha Devi D et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors AKM and DTS are the employees of Healthium Medtech Limited, India who are manufacturers of Trusynth fast suture. Author DHD, CB, PD and MBB declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
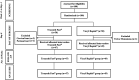
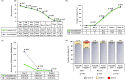
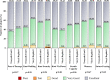
References
-
- Thukral P, Mendiratta S, Bhola G: A comparative study of subcuticular and interrupted stitches for episiotomy. Int. J. Reprod. Contraception, Obstet. Gynecol. 2018;7(5107):5107. 10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20184976 - DOI
-
- Perumal D, Selvaraju D: Comparative study of episiotomy repair: absorbable synthetic versus chromic catgut suture material. Int. J. Reprod. Contraception, Obstet. Gynecol. 2017;6:2186. 10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20172042 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

