Halogenated PETN derivatives: interplay between physical and chemical factors in explosive sensitivity
- PMID: 37389270
- PMCID: PMC10306076
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sc01627g
Halogenated PETN derivatives: interplay between physical and chemical factors in explosive sensitivity
Abstract
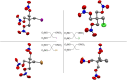
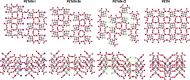
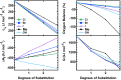
Determining the factors that influence and can help predict energetic material sensitivity has long been a challenge in the explosives community. Decades of literature reports identify a multitude of factors both chemical and physical that influence explosive sensitivity; however no unifying theory has been observed. Recent work by our team has demonstrated that the kinetics of "trigger linkages" (i.e., the weakest bonds in the energetic material) showed strong correlations with experimental drop hammer impact sensitivity. These correlations suggest that the simple kinetics of the first bonds to break are good indicators for the reactivity observed in simple handling sensitivity tests. Herein we report the synthesis of derivatives of the explosive pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN) in which one, two or three of the nitrate ester functional groups are substituted with an inert group. Experimental and computational studies show that explosive sensitivity correlates well with Q (heat of explosion), due to the change in the number of trigger linkages removed from the starting material. In addition, this correlation appears more significant than other observed chemical or physical effects imparted on the material by different inert functional groups, such as heat of formation, heat of explosion, heat capacity, oxygen balance, and the crystal structure of the material.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures







References
-
- Fickett W. and Davis W. C., Detonation Theory and Experiment. Dover Publications, 2011
-
- Yan Q.-L. Zeman S. Elbeih A. Song Z.-W. Malek J. The effect of crystal structure on the thermal reactivity of CL-20 and its C4 bonded explosives (I): thermodynamic properties and decomposition kinetics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013;112:823–836. doi: 10.1007/s10973-012-2711-x. - DOI
-
- Mueller K. F. Renner R. H. Gilligan W. H. Adolph H. G. Kamlet M. J. Thermal Stability/Structure Relations of Some Polynitroaliphatic Explosives. Combust. Flame. 1983;50:341–349. doi: 10.1016/0010-2180(83)90074-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

