Versatile multimodal modality based on Brillouin light scattering and the photoacoustic effect
- PMID: 37390147
- PMCID: PMC11426331
- DOI: 10.1364/OL.495361
Versatile multimodal modality based on Brillouin light scattering and the photoacoustic effect
Abstract
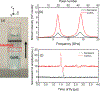
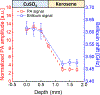
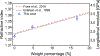
Multimodal optical techniques are useful for the comprehensive characterization of material properties. In this work, we developed a new, to the best of our knowledge, multimodal technology that can simultaneously measure a subset of mechanical, optical, and acoustical properties of the sample and is based on the integration of Brillouin (Br) and photoacoustic (PA) microscopy. The proposed technique can acquire co-registered Br and PA signals from the sample. Importantly, using synergistic measurements of the speed of sound and Brillouin shift, the modality offers a new approach to quantifying the optical refractive index, which is a fundamental property of a material and is not accessible by either technique individually. As a proof of concept, we demonstrated the feasibility of integrating the two modalities and acquired the colocalized Br and time-resolved PA signals in a synthetic phantom made out of kerosene and CuSO4 aqueous solution. In addition, we measured the refractive index values of saline solutions and validated the result. Comparison with previously reported data showed a relative error of 0.3%. This further allowed us to directly quantify the longitudinal modulus of the sample with the colocalized Brillouin shift. While the scope of the current work is limited to introducing the combined Br-PA setup for the first time, we envision that this multimodal modality could open a new path for the multi-parametric analysis of material properties.
Figures

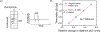
Update of
-
A versatile multimodal optical modality based on Brillouin light scattering and photoacoustic effect.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 12:2023.03.10.532144. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.10.532144. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Opt Lett. 2023 Jul 1;48(13):3427-3430. doi: 10.1364/OL.495361. PMID: 36945550 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A versatile multimodal optical modality based on Brillouin light scattering and photoacoustic effect.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 12:2023.03.10.532144. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.10.532144. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Opt Lett. 2023 Jul 1;48(13):3427-3430. doi: 10.1364/OL.495361. PMID: 36945550 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Multimodal quantitative optical elastography of the crystalline lens with optical coherence elastography and Brillouin microscopy.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Mar 17;11(4):2041-2051. doi: 10.1364/BOE.387361. eCollection 2020 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 32341865 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal imaging system combining optical coherence tomography and Brillouin microscopy for neural tube imaging.Opt Lett. 2022 Mar 15;47(6):1347-1350. doi: 10.1364/OL.453996. Opt Lett. 2022. PMID: 35290310 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating photoacoustic microscopy with other imaging technologies for multimodal imaging.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Apr;246(7):771-777. doi: 10.1177/1535370220977176. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33297735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noninvasive Imaging: Brillouin Confocal Microscopy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1092:351-364. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-95294-9_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30368760 Review.
References
-
- Bell AG, “The photophone,” Science, 130–134 (1880). - PubMed
-
- Xu M, and Wang LV, “Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 041101 (2006).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

