Single-cell profiling of lncRNA expression during Ebola virus infection in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 37391481
- PMCID: PMC10313701
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39627-7
Single-cell profiling of lncRNA expression during Ebola virus infection in rhesus macaques
Abstract
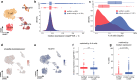
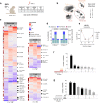
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in numerous biological processes and are pivotal mediators of the immune response, yet little is known about their properties at the single-cell level. Here, we generate a multi-tissue bulk RNAseq dataset from Ebola virus (EBOV) infected and not-infected rhesus macaques and identified 3979 novel lncRNAs. To profile lncRNA expression dynamics in immune circulating single-cells during EBOV infection, we design a metric, Upsilon, to estimate cell-type specificity. Our analysis reveals that lncRNAs are expressed in fewer cells than protein-coding genes, but they are not expressed at lower levels nor are they more cell-type specific when expressed in the same number of cells. In addition, we observe that lncRNAs exhibit similar changes in expression patterns to those of protein-coding genes during EBOV infection, and are often co-expressed with known immune regulators. A few lncRNAs change expression specifically upon EBOV entry in the cell. This study sheds light on the differential features of lncRNAs and protein-coding genes and paves the way for future single-cell lncRNA studies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SAB Biotherapeutics, Inc. provided the study materials from the study by Luke et al. None of the authors of this study has financial interest in SAB Biotherapeutics, Inc. company. P.C.S. is a co-founder of, shareholder in, and advisor to Sherlock Biosciences, Inc.; a board member of and shareholder in the Danaher Corporation; and a co-founder of and shareholder in Delve Bio. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

