The LongitudinAl Nationwide stuDy on Management And Real-world outComes of diabetes in India over 3 years (LANDMARC trial)
- PMID: 37392036
- PMCID: PMC10495555
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.422
The LongitudinAl Nationwide stuDy on Management And Real-world outComes of diabetes in India over 3 years (LANDMARC trial)
Abstract
Introduction: LANDMARC (CTRI/2017/05/008452), a prospective, observational real-world study, evaluated the occurrence of diabetes complications, glycemic control and treatment patterns in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from pan-India regions over a period of 3 years.
Methods: Participants with T2DM (≥25 to ≤60 years old at diagnosis, diabetes duration ≥2 years at the time of enrollment, with/without glycemic control and on ≥2 antidiabetic therapies) were included. The proportion of participants with macrovascular and microvascular complications, glycemic control and time to treatment adaptation over 36 months were assessed.
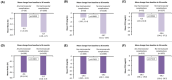
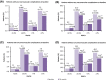
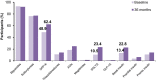
Results: Of the 6234 participants enrolled, 5273 completed 3 years follow-up. At the end of 3-years, 205 (3.3%) and 1121 (18.0%) participants reported macrovascular and microvascular complications, respectively. Nonfatal myocardial infarction (40.0%) and neuropathy (82.0%) were the most common complications. At baseline and 3-years, 25.1% (1119/4466) and 36.6% (1356/3700) of participants had HbA1c <7%, respectively. At 3-years, population with macrovascular and microvascular complications had higher proportion of participants with uncontrolled glycemia (78.2% [79/101] and 70.3% [463/659], respectively) than those without complications (61.6% [1839/2985]). Over 3-years, majority (67.7%-73.9%) of the participants were taking only OADs (biguanides [92.2%], sulfonylureas [77.2%] and DPP-IV inhibitors [62.4%]). Addition of insulin was preferred in participants who were only on OADs at baseline, and insulin use gradually increased from 25.5% to 36.7% at the end of 3 years.
Conclusion: These 3-year trends highlight the burden of uncontrolled glycemia and cumulative diabetes-related complications, emphasizing the importance of optimizing diabetes management in India.
Keywords: India; LANDMARC; T2DM; diabetes-related complications; glycemic control; real-world evidence; treatment pattern.
© 2023 Sanofi and The Authors. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
AKD, AM, AGU and NR received honoraria from Sanofi and other pharmaceutical companies. KMPK is on the advisory board of Sanofi and received honorarium for his talks. SJ received speaker/advisory/research grants from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Biocon, Boehringer Ingelheim (BI), Eli Lilly, Franco Indian, Glenmark, Lupin, Marico, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi, Serdia, Twinhealth and Zydus. SK received honoraria/speaker fees from Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. HT received honoraria from MSD, Novartis, Sanofi and from other companies for advice and lectures. BS received honorarium from Aventis, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, BI and MSD. SC received honoraria/grants from Biocon, BI, Intas, Novartis, Sanofi and Serdia. SKW has nothing to declare. AHZ received honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, BI and Sanofi. SKM, AG, ASugumaran, ASatpathy, RN, DC and CT are/were employees of Sanofi and may hold stock options.
Figures
References
-
- Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM, Mohan V. Diabetes mellitus and its complications in India. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(6):357‐370. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes in South‐East Asia‐2021 . Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/idfawp/resource‐files/2021/11/IDF‐Atlas‐Factsh.... Last accessed on: January 3. 2023.
-
- Anjana RM, Unnikrishnan R, Deepa M, et al. Achievement of guideline recommended diabetes treatment targets and health habits in people with self‐reported diabetes in India (ICMR‐INDIAB‐13): a national cross‐sectional study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(6):430‐441. - PubMed

