Type 2 cytokines and scleroderma interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 37392249
- PMCID: PMC10618297
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-023-01125-x
Type 2 cytokines and scleroderma interstitial lung disease
Abstract
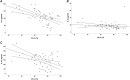
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a life-threatening complication of systemic sclerosis (SSc). Type 2 (Th2) cytokines play a pivotal role in airway disease. Study aim was to evaluate serum level of Th2 interleukin (IL) and chemokine in SSc-ILD. Serum levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-11, IL-13, IL-21, IL-31 and CXCL-13 were measured by Bio-Plex Multiplex Immunoassays in 60 SSc patients and 20 healthy controls (HC). Pulmonary function tests with diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DLco) and high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) were performed in SSc patients. ILD is defined as fibrotic changes (ground glass, reticular and honeycombing), assessed by Computer-Aided Lung Informatics for Pathology Evaluation and Ratings (CALIPER) software, affecting at least 10% of the lungs. Serum levels of Th2 cytokines were higher in SSc patients than HC. A linear correlation was observed between ground glass and IL-13 (r = 0.342, p < 0.01), IL-21 (r = 0.345, p < 0.01), IL-31 (r = 0.473, p < 0.001), IL-4 (r = 0.863, p < 0.001), IL-5 (r = 0.249, p < 0.05) and peripheral blood eosinophils (r = 0.463, p < 0.001). We found a negative correlation between DLco and IL-4 (r = - 0.511, p < 0.001) and peripheral blood eosinophils (r = - 0.446, p < 0.001). In the logistic regression analysis, IL-4 is associated with DLco ≤ 60% of the predicted [OR 1.039 (CI 95%: 1.015-1.064), p < 0.001], whilst mRSS [OR 1.138 (CI 95%: 1.023-1.266), p < 0.05] and IL-4 [OR 1.017 (CI 95%: 1-1.034), p < 0.05] were associated with ILD. Th2 inflammation could play a key role in early phase of SSc-ILD.
Keywords: CALIPER; Ground glass; Interstitial lung disease; Systemic sclerosis; Th2 cytokines.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

