Zeb1 and Tle3 are trans-factors that differentially regulate the expression of myosin heavy chain-embryonic and skeletal muscle differentiation
- PMID: 37392376
- PMCID: PMC7615532
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202201698RR
Zeb1 and Tle3 are trans-factors that differentially regulate the expression of myosin heavy chain-embryonic and skeletal muscle differentiation
Abstract
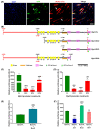
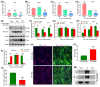
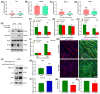
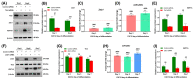
Myosin heavy chain-embryonic encoded by the Myh3 gene is a skeletal muscle-specific contractile protein expressed during mammalian development and regeneration, essential for proper myogenic differentiation and function. It is likely that multiple trans-factors are involved in this precise temporal regulation of Myh3 expression. We identify a 4230 bp promoter-enhancer region that drives Myh3 transcription in vitro during C2C12 myogenic differentiation and in vivo during muscle regeneration, including sequences both upstream and downstream of the Myh3 TATA-box that are necessary for complete Myh3 promoter activity. Using C2C12 mouse myogenic cells, we find that Zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (Zeb1) and Transducin-like Enhancer of Split 3 (Tle3) proteins are crucial trans-factors that interact and differentially regulate Myh3 expression. Loss of Zeb1 function results in earlier expression of myogenic differentiation genes and accelerated differentiation, whereas Tle3 depletion leads to reduced expression of myogenic differentiation genes and impaired differentiation. Tle3 knockdown resulted in downregulation of Zeb1, which could be mediated by increased expression of miR-200c, a microRNA that binds to Zeb1 transcript and degrades it. Tle3 functions upstream of Zeb1 in regulating myogenic differentiation since double knockdown of Zeb1 and Tle3 resulted in effects seen upon Tle3 depletion. We identify a novel E-box in the Myh3 distal promoter-enhancer region, where Zeb1 binds to repress Myh3 expression. In addition to regulation of myogenic differentiation at the transcriptional level, we uncover post-transcriptional regulation by Tle3 to regulate MyoG expression, mediated by the mRNA stabilizing Human antigen R (HuR) protein. Thus, Tle3 and Zeb1 are essential trans-factors that differentially regulate Myh3 expression and C2C12 cell myogenic differentiation in vitro.
Keywords: C2C12 cells; Tle3; Zeb1; mouse; myogenin; myosin heavy chain-embryonic; regeneration; skeletal muscle.
© 2023 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beylkin DH, Allen DL, Leinwand LA. MyoD, Myf5, and the calcineurin pathway activate the developmental myosin heavy chain genes. Dev Biol. 2006;294:541–553. - PubMed
-
- Daou N, Lecolle S, Lefebvre S, et al. A new role for the calcineurin/NFAT pathway in neonatal myosin heavy chain expression via the NFATc2/MyoD complex during mouse myogenesis. Development. 2013;140:4914–4925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

