TCR-independent CD137 (4-1BB) signaling promotes CD8+-exhausted T cell proliferation and terminal differentiation
- PMID: 37392737
- PMCID: PMC10649891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.06.007
TCR-independent CD137 (4-1BB) signaling promotes CD8+-exhausted T cell proliferation and terminal differentiation
Abstract
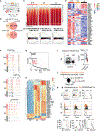
CD137 (4-1BB)-activating receptor represents a promising cancer immunotherapeutic target. Yet, the cellular program driven by CD137 and its role in cancer immune surveillance remain unresolved. Using T cell-specific deletion and agonist antibodies, we found that CD137 modulates tumor infiltration of CD8+-exhausted T (Tex) cells expressing PD1, Lag-3, and Tim-3 inhibitory receptors. T cell-intrinsic, TCR-independent CD137 signaling stimulated the proliferation and the terminal differentiation of Tex precursor cells through a mechanism involving the RelA and cRel canonical NF-κB subunits and Tox-dependent chromatin remodeling. While Tex cell accumulation induced by prophylactic CD137 agonists favored tumor growth, anti-PD1 efficacy was improved with subsequent CD137 stimulation in pre-clinical mouse models. Better understanding of T cell exhaustion has crucial implications for the treatment of cancer and infectious diseases. Our results identify CD137 as a critical regulator of Tex cell expansion and differentiation that holds potential for broad therapeutic applications.
Keywords: CD137 (TNFRSF9, 4-1BB); CD8(+) T lymphocytes; NF-κB signaling; T cell exhaustion; activation receptor; immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; tumor immune escape.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





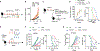
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

