Antidepressant effects of novel positive allosteric modulators of Trk-receptor mediated signaling - a potential therapeutic concept?
- PMID: 37394539
- PMCID: PMC10349764
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-023-06410-x
Antidepressant effects of novel positive allosteric modulators of Trk-receptor mediated signaling - a potential therapeutic concept?
Abstract
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is defined as a complex mental disorder which is characterized by a pervasive low mood and aversion to activity. Several types of neurotransmitter systems e.g. serotonergic, glutamatergic and noradrenergic systems have been suggested to play an important role in the origination of depression, but neurotrophins such as brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) have also been implicated in the disease process.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a newly developed class of molecules, characterized as positive allosteric modulators of neurotrophin/Trk receptor mediated signaling (Trk-PAM), on neurotransmitter release and depression-like behavior in vivo.
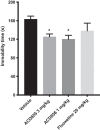
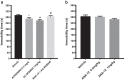
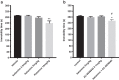
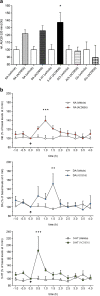
Methods: The effect of and possible interaction of neurotrophin/Trk signaling pathways with serotonergic and glutamatergic systems in the modulation of depression-related responses was studied using newly developed Trk-PAM compounds (ACD855, ACD856 and AC26845), as well as ketamine and fluoxetine in the forced swim test (FST) in rodents. Moreover, in vivo microdialysis in freely moving rats was used to assess changes in neurotransmitter levels in the rat.
Results: The results from the study show that several different compounds, which all potentiate Trk-receptor mediated signaling, display antidepressant-like activity in the FST. Moreover, the data also indicate that the effects of both fluoxetine and ketamine in the FST, both used in clinical practice, are mediated via BDNF/TrkB signaling, which could have implications for novel therapies in MDD.
Conclusions: Trk-PAMs could provide an interesting avenue for the development of novel therapeutics in this area.
Keywords: BDNF; Fluoxetine; Ketamine; MDD; Mice; Positive allosteric modulator; TrkB.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Nather Madjid, Veronica Lidell, Gunnar Nordvall, Pontus Forsell and Johan Sandin are employed by AlzeCure Pharma AB.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Potentiation of antidepressant effects: NPY1R agonist and ketamine synergy enhances TrkB signaling and neurogenesis in the ventral hippocampus.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024 Apr;28(4):309-322. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2024.2342524. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024. PMID: 38626283
-
Identification of Novel Positive Allosteric Modulators of Neurotrophin Receptors for the Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction.Cells. 2021 Jul 23;10(8):1871. doi: 10.3390/cells10081871. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440640 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of glutamate transporter 1 via BDNF-TrkB signaling plays a role in the anti-apoptotic and antidepressant effects of ketamine in chronic unpredictable stress model of depression.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Feb;233(3):405-15. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4128-2. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26514555
-
Role of a VGF/BDNF/TrkB Autoregulatory Feedback Loop in Rapid-Acting Antidepressant Efficacy.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jul;68(3):504-509. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1124-0. Epub 2018 Jul 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30022437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TrkB neurotrophin receptor at the core of antidepressant effects, but how?Cell Tissue Res. 2019 Jul;377(1):115-124. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-02985-6. Epub 2019 Jan 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2019. PMID: 30637517 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain region-specific roles of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in social stress-induced depressive-like behavior.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jan 1;20(1):159-173. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01419. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38767484 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective and Disease-Modifying Effects of the Triazinetrione ACD856, a Positive Allosteric Modulator of Trk-Receptors for the Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 6;24(13):11159. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311159. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446337 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted effects of fluoxetine treatment on cognitive functions.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 16;15:1412420. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1412420. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39081952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positive Allosteric Modulators of Trk Receptors for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 28;17(8):997. doi: 10.3390/ph17080997. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DSP-6745, a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine modulator with rapid antidepressant, anxiolytic, antipsychotic and procognitive effects.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Nov;241(11):2223-2239. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06629-2. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38856765
References
-
- Anelli M, Bizzi A, Caccia S, Codegoni AM, Fracasso C, Garattini S. Anorectic activity of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine in mice, rats and guinea-pigs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1992;44(8):696–698. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

