Environmental, mechanistic and evolutionary landscape of antibiotic persistence
- PMID: 37395716
- PMCID: PMC10398667
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.202357309
Environmental, mechanistic and evolutionary landscape of antibiotic persistence
Abstract
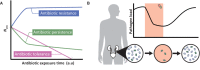
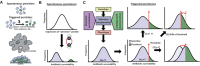
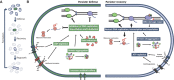
Recalcitrant infections pose a serious challenge by prolonging antibiotic therapies and contributing to the spread of antibiotic resistance, thereby threatening the successful treatment of bacterial infections. One potential contributing factor in persistent infections is antibiotic persistence, which involves the survival of transiently tolerant subpopulations of bacteria. This review summarizes the current understanding of antibiotic persistence, including its clinical significance and the environmental and evolutionary factors at play. Additionally, we discuss the emerging concept of persister regrowth and potential strategies to combat persister cells. Recent advances highlight the multifaceted nature of persistence, which is controlled by deterministic and stochastic elements and shaped by genetic and environmental factors. To translate in vitro findings to in vivo settings, it is crucial to include the heterogeneity and complexity of bacterial populations in natural environments. As researchers continue to gain a more holistic understanding of this phenomenon and develop effective treatments for persistent bacterial infections, the study of antibiotic persistence is likely to become increasingly complex.
Keywords: antibiotic persistence; evolution; persistent infections; persister recovery; tolerance.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ackermann M (2015) A functional perspective on phenotypic heterogeneity in microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 13: 497–508 - PubMed
-
- Alam MK, Alhhazmi A, DeCoteau JF, Luo Y, Geyer CR (2016) RecA inhibitors potentiate antibiotic activity and block evolution of antibiotic resistance. Cell Chem Biol 23: 381–391 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

