Saponarin, a Di-glycosyl Flavone from Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): An Effective Compound for Plant Defense and Therapeutic Application
- PMID: 37396229
- PMCID: PMC10308553
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00267
Saponarin, a Di-glycosyl Flavone from Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): An Effective Compound for Plant Defense and Therapeutic Application
Abstract
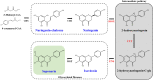
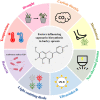
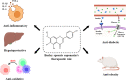
Saponarin (SA) is a major di-C-glycosyl-O-glycosyl flavone, which is predominantly accumulated in the young green leaves of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), with numerous biological functions in plants, such as protection against environmental stresses. Generally, SA synthesis and its localization in the mesophyll vacuole or leaf epidermis are largely stimulated in response to biotic and abiotic stresses to participate in a plant's defense response. In addition, SA is also credited for its pharmacological properties, such as the regulation of signaling pathways associated with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses. In recent years, many researchers have shown the potential of SA to treat oxidative and inflammatory disorders, such as in protection against liver diseases, and reducing blood glucose, along with antiobesity effects. This review aims to highlight natural variations of SA in plants, biosynthesis pathway, and SA's role in response to environmental stress and implications in various therapeutic applications. In addition, we also discuss the challenges and knowledge gaps concerning SA use and commercialization.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Flavonoid biosynthesis in barley primary leaves requires the presence of the vacuole and controls the activity of vacuolar flavonoid transport.Plant Physiol. 2007 May;144(1):432-44. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.094748. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17369433 Free PMC article.
-
Further knowledge on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) leaves O-glycosyl-C-glycosyl flavones by liquid chromatography-UV diode-array detection-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2008 Feb 22;1182(1):56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.12.070. Epub 2008 Jan 3. J Chromatogr A. 2008. PMID: 18215689
-
The mis-identification of the major antioxidant flavonoids in young barley (Hordeum vulgare) leaves.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2003 Jan-Feb;58(1-2):53-6. doi: 10.1515/znc-2003-1-209. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12622226
-
Therapeutic Potential of Young Green Barley Leaves in Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases: An Overview.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(7):1311-29. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500743. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26477798 Review.
-
Salicylic Acid as a Safe Plant Protector and Growth Regulator.Plant Pathol J. 2020 Feb;36(1):1-10. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.RW.12.2019.0295. Epub 2020 Feb 1. Plant Pathol J. 2020. PMID: 32089657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Validating the antiseizure effects of vitexin and related flavone glycosides in zebrafish.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1628324. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1628324. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40642006 Free PMC article.
-
Variation of Saponarin Content in Barley Sprouts (Hordeum vulgare L.) by Natural Light Shielding: Implication of the Importance of Light Intensity.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 20;8(39):35837-35844. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03458. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37810714 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Growth and Secondary Metabolites by the Combined Treatment of Trace Elements and Hydrogen Water in Wheat Sprouts.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 25;24(23):16742. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316742. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069065 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Abiotic Signals on the Accumulation of Saponarin in Barley Leaves in Hydroponics Under Artificial Lights.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 21;9(9):10852-10859. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09809. eCollection 2024 Mar 5. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38463256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hagiwara Y.; Hagiwara H.; Ueyama H. Physiologically active substances in young green barley leaf extract. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi. 2001, 48, 712–725. 10.3136/nskkk.48.712. - DOI
-
- Ferreres F.; Andrade P. B.; Valentao P.; Gil-Izquierdo A. Further knowledge on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) leaves O-glycosyl-C-glycosyl flavones by liquid chromatography-UV diode-array detection-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1182, 56–64. 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.12.070. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Simeonova R.; Vitcheva V.; Kondeva-Burdina M.; Krasteva I.; Manov V.; Mitcheva M. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of saponarin, isolated from Gypsophila trichotoma Wend. on paracetamol-induced liver damage in rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 757126.10.1155/2013/757126. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

