The miR-21-5p enriched in the apoptotic bodies of M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles alleviates osteoarthritis by changing macrophage phenotype
- PMID: 37396516
- PMCID: PMC10308169
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.09.010
The miR-21-5p enriched in the apoptotic bodies of M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles alleviates osteoarthritis by changing macrophage phenotype
Abstract
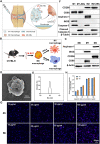
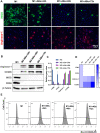
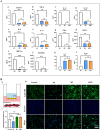
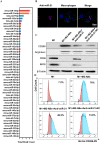
Macrophages (Mφs) play a crucial role in the pathological progression of osteoarthritis (OA) by regulating inflammation and tissue repair. Decreasing pro-inflammatory M1-Mφs and increasing anti-inflammatory M2-Mφs can alleviate OA-related inflammation and promote cartilage repair. Apoptosis is a natural process associated with tissue repair. A large number of apoptotic bodies (ABs), a type of extracellular vesicle, are produced during apoptosis, and this is associated with a reduction in inflammation. However, the functions of apoptotic bodies remain largely unknown. In this study, we investigated the role of M2-Mφs-derived apoptotic bodies (M2-ABs) in regulating the M1/M2 balance of macrophages in a mouse model of OA. Our data show that M2-ABs can be targeted for uptake by M1-Mφs, and this reprograms M1-to-M2 phenotypes within 24 h. The M2-ABs significantly ameliorated the severity of OA, alleviated the M1-mediated pro-inflammatory environment, and inhibited chondrocyte apoptosis in mice. RNA-seq revealed that M2-ABs were enriched with miR-21-5p, a microRNA that is negatively correlated with articular cartilage degeneration. Inhibiting the function of miR-21-5p in M1-Mφs significantly reduced M2-ABs-guided M1-to-M2 reprogramming following in vitro cell transfection. Together, these results suggest that M2-derived apoptotic bodies can prevent articular cartilage damage and improve gait abnormalities in OA mice by reversing the inflammatory response caused by M1 macrophages. The mechanism underlying these findings may be related to miR-21-5p-regulated inhibition of inflammatory factors. The application of M2-ABs may represent a novel cell therapy, and could provide a valuable strategy for the treatment of OA and/or chronic inflammation.
Keywords: Apoptotic body; Extracellular vesicles; Macrophage phenotype switch; MicroRNA-21; Osteoarthritis.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures
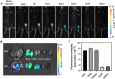
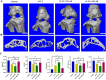
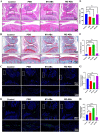
Similar articles
-
M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-26b-5p regulates macrophage polarization and chondrocyte hypertrophy by targeting TLR3 and COL10A1 to alleviate osteoarthritis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Feb 19;22(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02336-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38374072 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis via M2 macrophages.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jan 20;20(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01236-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35057811 Free PMC article.
-
M2 Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Encapsulated in Hyaluronic Acid Alleviate Osteoarthritis by Modulating Macrophage Polarization.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 May 13;10(5):3355-3377. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01833. Epub 2024 Apr 2. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 38563817
-
Macrophage: A Potential Target on Cartilage Regeneration.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 11;11:111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00111. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:708186. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.708186. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34456917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fibrous scaffolds loaded with BMSC-derived apoptotic vesicles promote wound healing by inducing macrophage polarization.Genes Dis. 2024 Aug 9;12(2):101388. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101388. eCollection 2025 Mar. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 39759117 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles as new players in chronic non-communicable diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 17;15:1479330. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1479330. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39896803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The communication role of extracellular vesicles in the osteoarthritis microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 17;16:1549833. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1549833. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40165965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracecellulr vesicles (EVs) microRNAs (miRNAs) derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in osteoarthritis (OA); detailed role in pathogenesis and possible therapeutics.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 27;11(3):e42258. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42258. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40007782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of apoptotic vesicles in modulating inflammation, immune responses, and tissue regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 1;23(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03278-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40170079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhu M. Immunological perspectives on spatial and temporal vaccine delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;178 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

