Lack of interferon regulatory factor 3 leads to anxiety/depression-like behaviors through disrupting the balance of neuronal excitation and inhibition in mice
- PMID: 37396521
- PMCID: PMC10308133
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.05.003
Lack of interferon regulatory factor 3 leads to anxiety/depression-like behaviors through disrupting the balance of neuronal excitation and inhibition in mice
Abstract
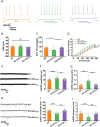
Disrupting the balance of neuronal excitation and inhibition (E/I) is an important pathogenic mechanism of anxiety and depression. Interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) plays a key role in the innate immune response, and activation of IRF3 triggers the expression of type I interferons and downstream interferon-stimulated genes, which are associated with anxiety and depression. However, whether IRF3 participates in the pathogenesis of anxiety/depression by regulating E/I balance remains poorly understood. Here, we reported that global knockout (KO) of IRF3 (IRF3-/-) significantly increased anxiety/depression-like behaviors, but did not affect normal spatial learning and memory. Compared with wild type (WT) control mice, the E/I balance was disrupted, as reflected by enhanced glutamatergic transmission and decreased GABAergic transmission in the neurons of hippocampal CA1 and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in IRF3-KO mice. Importantly, genetic rescue of IRF3 expression by adeno-associated virus (AAV) was sufficient to alleviate anxiety/depression-like behaviors and restore the neuronal E/I balance in IRF3-KO mice. Taken together, our results indicate that IRF3 is critical in maintaining neuronal E/I balance, thereby playing an essential role in ensuring emotional stability.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Hippocampus; IRF3; Medial prefrontal cortex; Synaptic transmission.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Huang Y., Wang Y., Wang H., et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(3):211–224. - PubMed
-
- Cosci F., Fava G.A. When anxiety and depression coexist: the role of differential diagnosis using clinimetric criteria. Psychother Psychosom. 2021;90(5):308–317. - PubMed
-
- Spijker J., Muntingh A., Batelaan N. Advice for clinicians on how to treat comorbid anxiety and depression. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(6):645–646. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

