LncRNA H19 mediates BMP9-induced angiogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by promoting the p53-Notch1 angiogenic signaling axis
- PMID: 37396541
- PMCID: PMC10308131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.04.013
LncRNA H19 mediates BMP9-induced angiogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by promoting the p53-Notch1 angiogenic signaling axis
Abstract
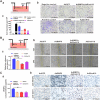
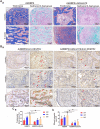
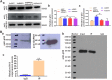
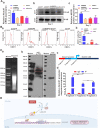
BMP9 mediated osteogenic differentiation mechanisms of MSCs were widely explored, however, mechanisms of BMP9-induced angiogenesis still need to be clarified. We previously characterized that Notch1 promoted BMP9-induced osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling process in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Here, we explored the underlying mechanisms of lncRNA H19 (H19) mediated regulation of BMP9-induced angiogenesis through activating Notch1 signaling. We demonstrated that basal expression level of H19 was high in MSCs, and silencing H19 attenuates BMP9-induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis of MSCs both in vitro and in vivo. Meanwhile, we identified that BMP9-induced production of CD31+ cells was indispensable for BMP9-induced bone formation, and silencing H19 dramatically blocked BMP9-induced production of CD31+ cells. In addition, we found that down-regulation of H19 inhibited BMP9 mediated blood vessel formation and followed subsequent bone formation in vivo. Mechanistically, we clarified that H19 promoted p53 phosphorylation by direct interacting and phosphorylating binding, and phosphorylated p53 potentiated Notch1 expression and activation of Notch1 targeting genes by binding on the promoter area of Notch1 gene. These findings suggested that H19 regulated BMP9-induced angiogenesis of MSCs by promoting the p53-Notch1 angiogenic signaling axis.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; BMP9; Bone tissue engineering; LncRNA H19; Mesenchymal stem cells.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Collon K., Gallo M.C., Lieberman J.R. Musculoskeletal tissue engineering: regional gene therapy for bone repair. Biomaterials. 2021;275:120901. - PubMed
-
- Liao J., Wei Q., Zou Y., et al. Notch signaling augments BMP9-induced bone formation by promoting the osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling process in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(5):1905–1923. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

