Efficacy of orally administered montmorillonite in myoglobinuric acute renal failure model in male rats
- PMID: 37396944
- PMCID: PMC10311980
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.67985.14866
Efficacy of orally administered montmorillonite in myoglobinuric acute renal failure model in male rats
Abstract
Objectives: Acute kidney injury can be associated with serious consequences and therefore early treatment is critical to decreasing mortality and morbidity rate. We evaluated the effect of montmorillonite, the clay with strong cation exchange capacity, on the AKI model in rats.
Materials and methods: Glycerol (50% solution, 10 ml/kg) was injected in the rat hind limbs to induce AKI. 24 hr after induction of acute kidney injury, the rats received oral doses of montmorillonite (0.5 g/kg or 1 g/kg), or sodium polystyrene sulfonate (1 g/kg) for three consecutive days.
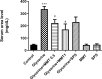
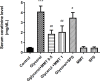
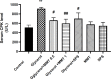
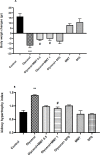
Results: Glycine induced acute kidney injury in rats with high levels of urea (336.60± 28.19 mg/dl), creatinine (4.10± 0.21 mg/dl), potassium (6.15 ± 0.28 mEq/L), and calcium (11.52 ± 0.19 mg/dl). Both doses of montmorillonite (0.5 and 1 g/kg) improved the serum urea (222.66± 10.02 and 170.20±8.06, P<0.05), creatinine (1.86±0.1, 2.05± 0.11, P<0.05), potassium (4.68 ± 0.4, 4.73 ± 0.34, P<0.001) and calcium (11.15 ± 0.17, 10.75 ± 0.25, P<0.01) levels. Treatment with montmorillonite especially at a high dose reduced the kidney pathological findings including, tubular necrosis, amorphous protein aggregation, and cell shedding into the distal and proximal tubule lumen. However, administration of SPS could not significantly decrease the severity of damages.
Conclusion: According to the results of this study, as well as the physicochemical properties of montmorillonite, such as high ion exchange capacity and low side effects, montmorillonite can be a low-cost and effective treatment option to reduce and improve the complications of acute kidney injury. However, the efficacy of this compound in human and clinical studies needs to be investigated.
Keywords: Acute renal failure; Bentonite; Clay; Kidney; Montmorillonite; Rhabdomyolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rahman M, Shad F, Smith MC. Acute kidney injury: A guide to diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:631–639. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
