DeepCTG® 1.0: an interpretable model to detect fetal hypoxia from cardiotocography data during labor and delivery
- PMID: 37397139
- PMCID: PMC10311205
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1190441
DeepCTG® 1.0: an interpretable model to detect fetal hypoxia from cardiotocography data during labor and delivery
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiotocography, which consists in monitoring the fetal heart rate as well as uterine activity, is widely used in clinical practice to assess fetal wellbeing during labor and delivery in order to detect fetal hypoxia and intervene before permanent damage to the fetus. We present DeepCTG® 1.0, a model able to predict fetal acidosis from the cardiotocography signals.
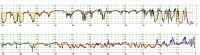
Materials and methods: DeepCTG® 1.0 is based on a logistic regression model fed with four features extracted from the last available 30 min segment of cardiotocography signals: the minimum and maximum values of the fetal heart rate baseline, and the area covered by accelerations and decelerations. Those four features have been selected among a larger set of 25 features. The model has been trained and evaluated on three datasets: the open CTU-UHB dataset, the SPaM dataset and a dataset built in hospital Beaujon (Clichy, France). Its performance has been compared with other published models and with nine obstetricians who have annotated the CTU-UHB cases. We have also evaluated the impact of two key factors on the performance of the model: the inclusion of cesareans in the datasets and the length of the cardiotocography segment used to compute the features fed to the model.
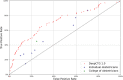
Results: The AUC of the model is 0.74 on the CTU-UHB and Beaujon datasets, and between 0.77 and 0.87 on the SPaM dataset. It achieves a much lower false positive rate (12% vs. 25%) than the most frequent annotation among the nine obstetricians for the same sensitivity (45%). The performance of the model is slightly lower on the cesarean cases only (AUC = 0.74 vs. 0.76) and feeding the model with shorter CTG segments leads to a significant decrease in its performance (AUC = 0.68 with 10 min segments).
Discussion: Although being relatively simple, DeepCTG® 1.0 reaches a good performance: it compares very favorably to clinical practice and performs slightly better than other published models based on similar approaches. It has the important characteristic of being interpretable, as the four features it is based on are known and understood by practitioners. The model could be improved further by integrating maternofetal clinical factors, using more advanced machine learning or deep learning approaches and having a more robust evaluation of the model based on a larger dataset with more pathological cases and covering more maternity centers.
Keywords: Fetal Heart Rate (FHR); cardiotocography; computerized cardiotocography; fetal hypoxia; fetal monitoring; fetal morbidity; fetal mortality; labor.
© 2023 Ben M'Barek, Jauvion, Vitrou, Holmström, Koskas and Ceccaldi.
Conflict of interest statement
GJ is the funder of Genos Care, a company building medical software. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zaima A. Intrapartum Fetal Monitoring Guideline.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

