Integrated metabolomics and peptidomics to delineate characteristic metabolites in milk fermented with novel Lactiplantibacillus plantarum L3
- PMID: 37397209
- PMCID: PMC10314206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100732
Integrated metabolomics and peptidomics to delineate characteristic metabolites in milk fermented with novel Lactiplantibacillus plantarum L3
Abstract
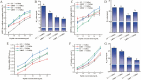
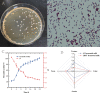
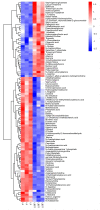
A novel wild-type Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) L3 with good fermentation characteristics and protein degradation capacity was isolated from raw milk samples. In this study, the metabolites in milk fermented with L. plantarum L3 were investigated by metabolomic and peptidomics analyses. The metabolomics results revealed that the metabolites in milk fermented with L. plantarum L3 were Thr-Pro, Val-Lys, l-creatine, pyridoxine, and muramic acid, which improved the taste and nutritional qualities of the milk. Moreover, the water-soluble peptides derived from L3 fermented milk exhibited high antioxidant properties and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory (ACEI) activities. Additionally, 152 peptides were found using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Furthermore, endogenous enzymes secreted by L. plantarum L3 cleaved β- and α-casein to release six ACEI peptides (ACEIPs), nineteen antioxidant peptides (AOPs), and five antimicrobial peptides (AMPS). Overall, these findings could be valuable in improving the quality of fermented milk.
Keywords: Bioactive peptides; Enzyme cleavage site; Fermented milk; Lactiplantibacillus plantarum L3; Metabolites.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Bioaccessible peptides released by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of fermented goat milks.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Jun;410(15):3597-3606. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-0983-0. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29523944
-
Metabolomic profile of milk fermented with Streptococcus thermophilus cocultured with Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, or both during storage.J Dairy Sci. 2021 Aug;104(8):8493-8505. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20270. Epub 2021 May 21. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 34024601
-
Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides in Goat Milk Fermented by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Food and Breast Milk.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2022 Jan;42(1):46-60. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2021.e55. Epub 2022 Jan 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2022. PMID: 35028573 Free PMC article.
-
A novel approach to Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: From probiotic properties to the omics insights.Microbiol Res. 2023 Mar;268:127289. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127289. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Microbiol Res. 2023. PMID: 36571922 Review.
-
β-Glucosidase Activity of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: A Key Player in Food Fermentation and Human Health.Foods. 2025 Apr 22;14(9):1451. doi: 10.3390/foods14091451. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Insight into Microbial Exploitation to Produce Bioactive Molecules from Agrifood and By-Products' Fermentation.Foods. 2025 Apr 21;14(8):1439. doi: 10.3390/foods14081439. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40282840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into characteristic metabolites and potential bioactive peptides profiles of fresh cheese fermented with three novel probiotics based metabolomics and peptidomics.Food Chem X. 2024 Jan 18;21:101147. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101147. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38312486 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Strategy for Mixed Jam Evaluation: Apparent Indicator, Sensory, Metabolomic, and GC-IMS Analysis.Foods. 2024 Apr 3;13(7):1104. doi: 10.3390/foods13071104. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38611408 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity and Peptidomic Analysis of Halotolerant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CH.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Mar 11. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10504-7. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40069511
References
-
- AOAC . 17th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Washington, DC: 1997. Official methods of analysis.
-
- Ayyash M., Al-Nuaimi A.K., Al-Mahadin S., Liu S.Q. In vitro investigation of anticancer and ace-inhibiting activity, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition, and antioxidant activity of camel milk fermented with camel milk probiotic: a comparative study with fermented bovine milk. Food Chemistry. 2018;239(15):588–597. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.149. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

