The digital edge: examining the relationship between digital competency and language learning outcomes
- PMID: 37397293
- PMCID: PMC10313065
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1187909
The digital edge: examining the relationship between digital competency and language learning outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: Technology in education, including language learning, is on the rise. Digital competency is essential for teachers to effectively integrate technology and enhance language teaching. It enables access to authentic materials, interactive exercises, and collaboration opportunities. However, integrating technology poses challenges for teachers.
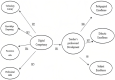
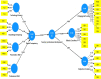
Objective: This empirical research aimed to investigate the impact of digital competency on language learning outcomes in the context of "smart education," which incorporates sustainable practices and digital technologies in the language classroom.
Methods: The study adopted a quantitative approach to collect and analyze data. The sample population for the study comprised of 344 language teachers at various language schools in a metropolitan city. The data collection carried out with a digital competency questionnaire. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multivariate technique, i.e., structural equation modeling.
Findings: The study found that digital competency positively correlated with language proficiency outcomes. Participants with higher levels of digital competency achieved better language learning outcomes compared to those with lower levels of digital competency. Additionally, the study found that incorporating sustainable practices, such as digitalized learning materials and virtual classrooms, positively contributed to language learning outcomes. The findings of this study suggest that digital competency plays a vital role in language learning outcomes in the context of "smart education."
Discussion & recommendation: Teachers should consider incorporating digital tools and sustainable practices into their language teaching to enhance language learning outcomes. The study recommends that language educators should focus on developing digital competency and integrating sustainable practices into their language classroom to promote effective language learning.
Keywords: didactic excellence; digital competency; educational methodologies; educational technology; knowledge deepening; pedagogical excellence; subjective excellence; technology literacy.
Copyright © 2023 Cao, Bhuvaneswari, Arumugam and Aravind.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abykanova B., Tashkeyeva G., Idrissov S., Bilyalova Z., Sadirbekova D. (2016). Professional competence of a teacher in higher educational institution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 11, 2197–2206. doi: 10.12973/ijese.2016.560a - DOI
-
- Agustini K., Santyasa I. W., Ratminingsih N. M. (2019). Analysis of competence on “TPACK”: 21st century teacher professional development. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1387:012035. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1387/1/012035 - DOI
-
- Ahmed W., Hizam S. M., Sentosa I. (2022). Digital dexterity: employee as consumer approach towards organizational success. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 25, 631–641. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2020.1835107 - DOI
-
- Akkuzu N. (2014). The role of different types of feedback in the reciprocal interaction of teaching performance and self-efficacy belief. Austral. J. Teach. Educ. 39, 37–66. doi: 10.14221/ajte.2014v39n3.3 - DOI
-
- Al Khateeb A. A. M. (2017). Measuring digital competence and ICT literacy: an exploratory study of in-service English language teachers in the context of Saudi Arabia. Int. Educ. Stud. 10, 38–51. doi: 10.5539/ies.v10n12p38 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources