Combatting negative bias: a mental contrasting and implementation intentions online intervention to increase help-seeking among individuals with elevated depressive symptomatology
- PMID: 37397325
- PMCID: PMC10310967
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1145969
Combatting negative bias: a mental contrasting and implementation intentions online intervention to increase help-seeking among individuals with elevated depressive symptomatology
Abstract
Background: There are many reasons why individuals with depression may not seek help. Among those with elevated depressive symptomatology, some previous interventions aimed at increasing help-seeking have unintentionally decreased help-seeking intentions. Beck's cognitive theory of depression posits that individuals with elevated depressive symptomatology process information differently from those without depression (i.e., increased cognitive errors, negative bias); potentially explaining the iatrogenic results of previous interventions. Mental contrasting and implementation intentions (MCII; a self-regulatory strategy) interventions have successfully influenced physical and mental health behaviors. However, MCII has not been used specifically for initiating help-seeking for depression. The goal of this research was to ascertain whether an online MCII intervention could increase actual help-seeking or the intention to seek help for depression.
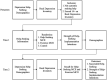
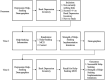
Method: Two online randomized pre-post experiments were conducted to measure the primary outcome measures 2 weeks post-intervention (Study 1 collected Summer 2019: information-only control ["C"], help-seeking MCII intervention ["HS"], and comparison MCII intervention ["E"]; Study 2 collected Winter 2020: "C" and "HS"). At Time 1, adults recruited from MTurk had a minimum Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) score of 14 (mild depressive symptoms) and were not seeking professional help.
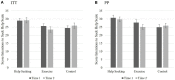
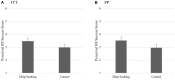
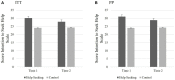
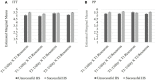
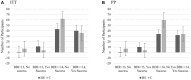
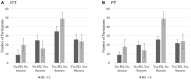
Results: Study 1 (N = 74) indicated that the intervention was feasible, provided preliminary support, and clarified intervention components for Study 2. Study 2 (N = 224) indicated that the HS group reported greater intentions to seek help and actual help-seeking than the C group. Proportionally, actual help-seeking was more likely among individuals who received the HS intervention and either did not perceive themselves as depressed at Time 2 or had BDI-II scores indicating that their depressive symptomatology decreased from Time 1.
Limitations: Participation was limited to US residents who self-reported data.
Discussion: These studies indicate that a brief online MCII intervention to encourage help-seeking is feasible and preliminarily successful. Future studies should consider using ecological momentary assessment measurements to establish the temporal precedence of intervention effects and whether MCII is effective for encouraging help-seeking among individuals prone to experiencing cognitive errors who may not be experiencing negative bias (e.g., bipolar disorder or anxiety). Clinicians may find this method successful in encouraging ongoing treatment engagement.
Keywords: MCII; depression; help-seeking; implementation intentions; mental contrasting; negative bias; online intervention.
Copyright © 2023 Keeler, Nydegger and Crano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interventions to improve mental help-seeking behaviours in individuals with depressive symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 May 23;25(1):528. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06976-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40410702 Free PMC article.
-
A brief intervention to improve exercising in patients with schizophrenia: a controlled pilot study with mental contrasting and implementation intentions (MCII).BMC Psychiatry. 2015 Sep 3;15:211. doi: 10.1186/s12888-015-0513-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26335438 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An online randomised controlled trial of mental contrasting with implementation intentions as a smoking behaviour change intervention.Psychol Health. 2020 Mar;35(3):318-345. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2019.1634200. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Psychol Health. 2020. PMID: 31264451 Clinical Trial.
-
The paradox of the resident experiencing depression: Higher depression, less favorable help-seeking outcome expectations, and lower help-seeking intentions.Soc Sci Med. 2024 Mar;344:116593. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2024.116593. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Soc Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38301547
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Mental Contrasting With Implementation Intentions on Goal Attainment.Front Psychol. 2021 May 12;12:565202. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.565202. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34054628 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Application of "Internet +" continuous emotion management training in patients with depression.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 26;15:1452717. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1452717. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39659552 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve mental help-seeking behaviours in individuals with depressive symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 May 23;25(1):528. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06976-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40410702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armitage C. J., Rahim W. A., Rowe R., O'Connor R. C. (2016). An exploratory randomised trial of a simple, brief psychological intervention to reduce subsequent suicidal ideation and behaviour in patients admitted to hospital for self-harm. Br. J. Psychiatry 208, 470–476. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.114.162495, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bayer U. C., Achtziger A., Gollwitzer P. M., Moskowitz G. B. (2009). Responding to subliminal cues: do if-then plans facilitate action preparation and initiation without conscious intent? Soc. Cogn. 27, 183–201. doi: 10.1521/soco.2009.27.2.183 - DOI
-
- Beck A. T. (1967) Depression: clinical, experimental, and theoretical aspects. New York: Hoeber Medical Division, Harper & Row.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

