Therapeutic strategies to recover ependymal barrier after inflammatory damage: relevance for recovering neurogenesis during development
- PMID: 37397456
- PMCID: PMC10308384
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1204197
Therapeutic strategies to recover ependymal barrier after inflammatory damage: relevance for recovering neurogenesis during development
Abstract
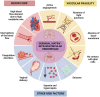
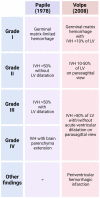
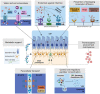
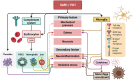
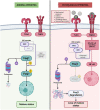
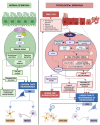
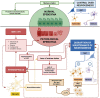
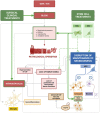
The epithelium covering the surfaces of the cerebral ventricular system is known as the ependyma, and is essential for maintaining the physical and functional integrity of the central nervous system. Additionally, the ependyma plays an essential role in neurogenesis, neuroinflammatory modulation and neurodegenerative diseases. Ependyma barrier is severely affected by perinatal hemorrhages and infections that cross the blood brain barrier. The recovery and regeneration of ependyma after damage are key to stabilizing neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative processes that are critical during early postnatal ages. Unfortunately, there are no effective therapies to regenerate this tissue in human patients. Here, the roles of the ependymal barrier in the context of neurogenesis and homeostasis are reviewed, and future research lines for development of actual therapeutic strategies are discussed.
Keywords: FoxJ1; cell therapy; ependyma; germinal matrix hemorrhage; neural stem cell; neurogenesis; neurogenic niche; posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus.
Copyright © 2023 Paez-Gonzalez, Sebastian, Ceron-Funez, Jimenez and Rodríguez-Perez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

