Unilateral caudate inactivation increases motor impulsivity in rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 37397813
- PMCID: PMC10313876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100085
Unilateral caudate inactivation increases motor impulsivity in rhesus monkeys
Abstract
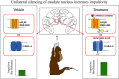
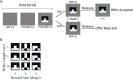
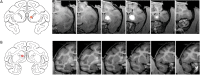
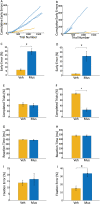
Impulsivity, the tendency to react quickly and without consideration of consequences, is correlated with asymmetry in the volume of the caudate nucleus in human patients. In this study, we sought to determine whether the induction of functional asymmetry in the caudate nucleus of monkeys would produce phenomenologically comparable behavior. We found that unilateral suppression of the ventral caudate nucleus increases impulsive behavior in rhesus monkeys. Impulsivity was modeled by the subjects' inability to maintain hold of a touch-sensitive bar until presentation of an imperative signal. Two methods were used to suppress activity in the caudate region. First, muscimol was locally infused. Second, a viral construct expressing the hM4Di DREADD (designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drug) was injected at the same site. Clozapine N-oxide and deschloroclozapine activate the DREADD to suppress neuronal activity. Both methods of suppression, pharmacological and chemogenetic, increased the rate of early bar releases, a behavior we interpret to indicate impulsivity. Thus, we demonstrate a causal relationship between caudate asymmetry and impulsivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. 2013.
-
- Brewer J.A., Potenza M.N. The neurobiology and genetics of impulse control disorders: relationships to drug addictions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008;75(1):63–75. Dang, L. C., Samanez-Larkin, G. R., Young, J. S., Cowan, R. L., Kessler, R. M., & Zald, D. H. (2016). Caudate asymmetry is related to attentional impulsivity and an objective measure of ADHD-like attentional problems in healthy adults. Brain Structure and Function, 221(1), 277-286. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dang L.C., Samanez-Larkin G.R., Young J.S., Cowan R.L., Kessler R.M., Zald D.H. Caudate asymmetry is related to attentional impulsivity and an objective measure of ADHD-like attentional problems in healthy adults. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016;221:277–286. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0906-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

