This is a preprint.
The landscape of cancer rewired GPCR signaling axes
- PMID: 37398064
- PMCID: PMC10312480
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.03.13.532291
The landscape of cancer rewired GPCR signaling axes
Update in
-
The landscape of cancer-rewired GPCR signaling axes.Cell Genom. 2024 May 8;4(5):100557. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100557. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 38723607 Free PMC article.
Abstract
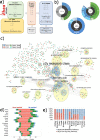
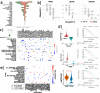
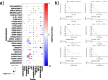
We explored the dysregulation of GPCR ligand signaling systems in cancer transcriptomics datasets to uncover new therapeutics opportunities in oncology. We derived an interaction network of receptors with ligands and their biosynthetic enzymes, which revealed that multiple GPCRs are differentially regulated together with their upstream partners across cancer subtypes. We showed that biosynthetic pathway enrichment from enzyme expression recapitulated pathway activity signatures from metabolomics datasets, providing valuable surrogate information for GPCRs responding to organic ligands. We found that several GPCRs signaling components were significantly associated with patient survival in a cancer type-specific fashion. The expression of both receptor-ligand (or enzymes) partners improved patient stratification, suggesting a synergistic role for the activation of GPCR networks in modulating cancer phenotypes. Remarkably, we identified many such axes across several cancer molecular subtypes, including many pairs involving receptor-biosynthetic enzymes for neurotransmitters. We found that GPCRs from these actionable axes, including e.g., muscarinic, adenosine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and chemokine receptors, are the targets of multiple drugs displaying anti-growth effects in large-scale, cancer cell drug screens. We have made the results generated in this study freely available through a webapp (gpcrcanceraxes.bioinfolab.sns.it).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest JSG reports consulting fees from Domain Pharmaceuticals, Pangea Therapeutics, and io9, and is founder of Kadima Pharmaceuticals, all unrelated to the current study.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
