This is a preprint.
A subtle structural modification of a synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist drastically increases its efficacy at the CB1 receptor
- PMID: 37398099
- PMCID: PMC10312643
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.10.544442
A subtle structural modification of a synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist drastically increases its efficacy at the CB1 receptor
Update in
-
Subtle Structural Modification of a Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist Drastically Increases its Efficacy at the CB1 Receptor.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Nov 1;14(21):3928-3940. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00530. Epub 2023 Oct 17. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37847546 Free PMC article.
Abstract
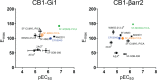
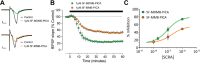
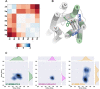
The emergence of synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) as illicit psychoactive substances has posed considerable public health risks that include fatalities. Many SCRAs exhibit much higher efficacy and potency, compared with the phytocannabinoid Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), at the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R), a G protein-coupled receptor involved in modulating neurotransmitter release. In this study, we investigated structure activity relationships (SAR) of aminoalkylindole SCRAs at CB1Rs, focusing on 5F-pentylindoles containing an amide linker attached to different head moieties. Using in vitro bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) assays, we identified a few of SCRAs exhibiting significantly higher efficacy in engaging the Gi protein and recruiting β-arrestin than the reference CB1R full agonist CP55940. Importantly, adding a methyl group at the head moiety of 5F-MMB-PICA yielded 5F-MDMB-PICA, an agonist exhibiting a large increase in efficacy and potency at the CB1R. This pharmacological observation was supported by a functional assay of the effects of these SCRAs on glutamate field potentials recorded in hippocampal slices. Molecular modeling and simulations of the CB1R bound with either of the SCRAs revealed critical structural determinants contributing to the higher efficacy of 5F-MDMB-PICA, and how these subtle differences propagated to the receptor-G protein interface. Thus, we find that apparently minor structural changes in the head moiety of SCRAs can cause major changes in efficacy. Our results highlight the need for close monitoring of structural modifications of newly emerging SCRAs and their potential for toxic drug responses in humans.
Keywords: bioluminescence resonance energy transfer; cannabinoid receptor 1; molecular dynamics; synthetic cannabinoids.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Huffman JW, Dai D., Martin B.R., Compton D.R.: Design, synthesis and pharmacology of cannabimimetic indoles. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 1994, 4(4):563–566.
-
- Wiley JL, Compton DR, Dai D, Lainton JA, Phillips M, Huffman JW, Martin BR: Structure-activity relationships of indole- and pyrrole-derived cannabinoids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998, 285(3):995–1004. - PubMed
-
- Usui K, Fujita Y, Kamijo Y, Kokaji T, Funayama M: Identification of 5-Fluoro ADB in Human Whole Blood in Four Death Cases. J Anal Toxicol 2018, 42(2):e21–e25. - PubMed
-
- Adams AJ, Banister SD, Irizarry L, Trecki J, Schwartz M, Gerona R: “Zombie” Outbreak Caused by the Synthetic Cannabinoid AMB-FUBINACA in New York. N Engl J Med 2017, 376(3):235–242. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
