This is a preprint.
Small Molecule in situ Resin Capture - A Compound First Approach to Natural Product Discovery
- PMID: 37398257
- PMCID: PMC10312467
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.03.02.530684
Small Molecule in situ Resin Capture - A Compound First Approach to Natural Product Discovery
Update in
-
Small molecule in situ resin capture provides a compound first approach to natural product discovery.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 19;15(1):5230. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49367-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38898025 Free PMC article.
Abstract
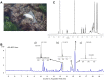
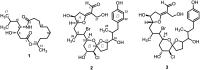
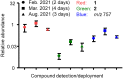
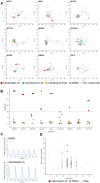
Microbial natural products remain an important resource for drug discovery. Yet, commonly employed discovery techniques are plagued by the rediscovery of known compounds, the relatively few microbes that can be cultured, and laboratory growth conditions that do not elicit biosynthetic gene expression among myriad other challenges. Here we introduce a culture independent approach to natural product discovery that we call the Small Molecule In situ Resin Capture (SMIRC) technique. SMIRC exploits in situ environmental conditions to elicit compound production and represents a new approach to access poorly explored chemical space by capturing natural products directly from the environments in which they are produced. In contrast to traditional methods, this compound-first approach can capture structurally complex small molecules across all domains of life in a single deployment while relying on Nature to provide the complex and poorly understood environmental cues needed to elicit biosynthetic gene expression. We illustrate the effectiveness of SMIRC in marine habitats with the discovery of numerous new compounds and demonstrate that sufficient compound yields can be obtained for NMR-based structure assignment. Two new compound classes are reported including one novel carbon skeleton that possesses a functional group not previously observed among natural products and a second that possesses potent biological activity. We introduce expanded deployments, in situ cultivation, and metagenomics as methods to facilitate compound discovery, enhance yields, and link compounds to producing organisms. This compound first approach can provide unprecedented access to new natural product chemotypes with broad implications for drug discovery.
Keywords: Biological sciences – biochemistry; Physical sciences – chemistry; drug discovery; environmental metabolomics; microbiomes; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement: The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Berdy J., Bioactive microbial metabolites. A personal view. J Antibiot 58, 1–26 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Anonymous (2021) World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines – 22nd List. (World Health Organization, Geneva: ), pp 1–66.
-
- Baltz R. H., Marcel Faber Roundtable: is our antibiotic pipeline unproductive because of starvation, constipation or lack of inspiration? J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 507–513 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Koehn F. E., Carter G. T., The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4, 206–220 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
