This is a preprint.
Analysis of a macrophage carbamylated proteome reveals a function in post-translational modification crosstalk
- PMID: 37398265
- PMCID: PMC10312928
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3044777/v1
Analysis of a macrophage carbamylated proteome reveals a function in post-translational modification crosstalk
Update in
-
Analysis of a macrophage carbamylated proteome reveals a function in post-translational modification crosstalk.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 18;21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01257-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37723562 Free PMC article.
Abstract
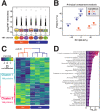
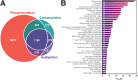
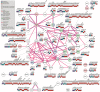
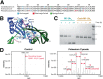
Background. Lysine carbamylation is a biomarker of rheumatoid arthritis and kidney diseases. However, its cellular function is understudied due to the lack of tools for systematic analysis of this post-translational modification (PTM). Methods. We adapted a method to analyze carbamylated peptides by co-affinity purification with acetylated peptides based on the cross-reactivity of anti-acetyllysine antibodies. We integrated this method into a mass spectrometry-based multi-PTM pipeline to simultaneously analyze carbamylated and acetylated peptides in addition to phosphopeptides were enriched by sequential immobilized-metal affinity chromatography. Results. By testing the pipeline with RAW 264.7 macrophages treated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide, 7,299, 8,923 and 47,637 acetylated, carbamylated, and phosphorylated peptides were identified, respectively. Our analysis showed that carbamylation occurs on proteins from a variety of functions on sites with similar as well as distinct motifs compared to acetylation. To investigate possible PTM crosstalk, we integrated the carbamylation data with acetylation and phosphorylation data, leading to the identification 1,183 proteins that were modified by all 3 PTMs. Among these proteins, 54 had all 3 PTMs regulated by lipopolysaccharide and were enriched in immune signaling pathways, and in particular, the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. We found that carbamylation of linear diubiquitin blocks the activity of the anti-inflammatory deubiquitinase OTULIN. Conclusions Overall, our data show that anti-acetyllysine antibodies can be used for effective enrichment of carbamylated peptides. Moreover, carbamylation may play a role in PTM crosstalk with acetylation and phosphorylation, and that it is involved in regulating ubiquitination in vitro .
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of a macrophage carbamylated proteome reveals a function in post-translational modification crosstalk.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 18;21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01257-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37723562 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Protocol to Simultaneously Study Protein Phosphorylation, Acetylation, and N-Linked Sialylated Glycosylation.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2261:55-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1186-9_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33420984
-
Evolution of anti-modified protein antibody responses can be driven by consecutive exposure to different post-translational modifications.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Dec 8;23(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02687-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34876234 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Posttranslational Modification in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focusing on Citrullination, Carbamylation, and Acetylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10576. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910576. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification, Quantification, and Site Localization of Protein Posttranslational Modifications via Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;919:345-382. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41448-5_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27975226 Review.
References
-
- Delanghe S, Delanghe JR, Speeckaert R, Van Biesen W, Speeckaert MM. Mechanisms and consequences of carbamoylation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:580–93. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Nicholls SJ, Rodriguez ER, Kummu O, Horkko S, Barnard J, Reynolds WF, Topol EJ, DiDonato JA, Hazen SL. Protein carbamylation links inflammation, smoking, uremia and atherogenesis. Nat Med. 2007;13:1176–84. - PubMed
-
- Jaisson S, Pietrement C, Gillery P. Protein Carbamylation: Chemistry, Pathophysiological Involvement, and Biomarkers. Adv Clin Chem. 2018;84:1–38. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

