This is a preprint.
H3.3-G34R Mutation-Mediated Epigenetic Reprogramming Leads to Enhanced Efficacy of Immune Stimulatory Gene Therapy in Diffuse Hemispheric Gliomas
- PMID: 37398299
- PMCID: PMC10312611
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.13.544658
H3.3-G34R Mutation-Mediated Epigenetic Reprogramming Leads to Enhanced Efficacy of Immune Stimulatory Gene Therapy in Diffuse Hemispheric Gliomas
Abstract
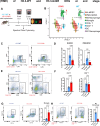
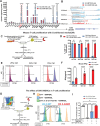
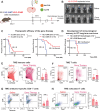
Diffuse hemispheric glioma (DHG), H3 G34-mutant, representing 9-15% of cases, are aggressive Central Nervous System (CNS) tumors with poor prognosis. This study examines the role of epigenetic reprogramming of the immune microenvironment and the response to immune-mediated therapies in G34-mutant DHG. To this end, we utilized human G34-mutant DHG biopsies, primary G34-mutant DHG cultures, and genetically engineered G34-mutant mouse models (GEMMs). Our findings show that the G34 mutation alters histone marks' deposition at promoter and enhancer regions, leading to the activation of the JAK/STAT pathway, which in turn results in an immune-permissive tumor microenvironment. The implementation of Ad-TK/Ad-Flt3L immunostimulatory gene therapy significantly improved median survival, and lead to over 50% long term survivors. Upon tumor rechallenge in the contralateral hemisphere without any additional treatment, the long-term survivors exhibited robust anti-tumor immunity and immunological memory. These results indicate that immune-mediated therapies hold significant potential for clinical translation in treating patients harboring H3.3-G34 mutant DHGs, offering a promising strategy for improving outcomes in this challenging cancer subtype affecting adolescents and young adults (AYA).
Statement of significance: This study uncovers the role of the H3.3-G34 mutation in reprogramming the tumor immune microenvironment in diffuse hemispheric gliomas. Our findings support the implementation of precision medicine informed immunotherapies, aiming at improving enhanced therapeutic outcomes in adolescents and young adults harboring H3.3-G34 mutant DHGs.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
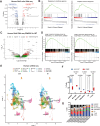

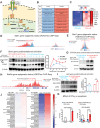
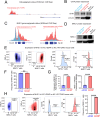
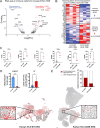
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 NS122536/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS123879/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS082311/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS124167/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA243916/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS110703/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076991/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES017885/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA261717/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS094804/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA221747/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS096756/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS122234/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA264338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS105556/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
