This is a preprint.
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
- PMID: 37398436
- PMCID: PMC10312674
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544560
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
Update in
-
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor.Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Apr;20(4):428-457. doi: 10.1038/s44320-024-00019-8. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Mol Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 38467836 Free PMC article.
Abstract
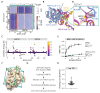
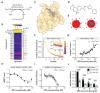
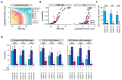
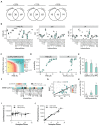
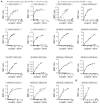
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) offer great opportunities to expand the druggable proteome and therapeutically tackle various diseases, but remain challenging targets for drug discovery. Here, we provide a comprehensive pipeline that combines experimental and computational tools to identify and validate PPI targets and perform early-stage drug discovery. We have developed a machine learning approach that prioritizes interactions by analyzing quantitative data from binary PPI assays and AlphaFold-Multimer predictions. Using the quantitative assay LuTHy together with our machine learning algorithm, we identified high-confidence interactions among SARS-CoV-2 proteins for which we predicted three-dimensional structures using AlphaFold Multimer. We employed VirtualFlow to target the contact interface of the NSP10-NSP16 SARS-CoV-2 methyltransferase complex by ultra-large virtual drug screening. Thereby, we identified a compound that binds to NSP10 and inhibits its interaction with NSP16, while also disrupting the methyltransferase activity of the complex, and SARS-CoV-2 replication. Overall, this pipeline will help to prioritize PPI targets to accelerate the discovery of early-stage drug candidates targeting protein complexes and pathways.
Keywords: AlphaFold; SARS-CoV-2; VirtualFlow; machine learning; protein-protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE AND COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
AI-guided pipeline for protein-protein interaction drug discovery identifies a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor.Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Apr;20(4):428-457. doi: 10.1038/s44320-024-00019-8. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Mol Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 38467836 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi-Pronged Approach Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Using Ultra-Large Virtual Screening.ChemRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 24. doi: 10.26434/chemrxiv.12682316. ChemRxiv. 2020. Update in: iScience. 2021 Feb 19;24(2):102021. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.102021. PMID: 33200116 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Virtual screening, ADME/T, and binding free energy analysis of anti-viral, anti-protease, and anti-infectious compounds against NSP10/NSP16 methyltransferase and main protease of SARS CoV-2.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020 Dec;40(6):605-612. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1772298. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020. PMID: 32476594 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the SARS-CoV-2-Host Protein-Protein Interactome by Affinity Purification Mass Spectrometry and Proximity-Dependent Biotin Labeling: A Rational and Straightforward Route to Discover Host-Directed Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 7;22(2):532. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020532. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico structure-based approaches to discover protein-protein interaction-targeting drugs.Methods. 2017 Dec 1;131:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28802714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alhossary A, Handoko SD, Mu Y & Kwoh C-K (2015) Fast, accurate, and reliable molecular docking with QuickVina 2. Bioinformatics 31: 2214–2216 - PubMed
-
- Araujo MEG de, Naschberger A, Fürnrohr BG, Stasyk T, Dunzendorfer-Matt T, Lechner S, Welti S, Kremser L, Shivalingaiah G, Offterdinger M, et al. (2017) Crystal structure of the human lysosomal mTORC1 scaffold complex and its impact on signaling. Science 358: 377–381 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
