SUMOylation at the inner nuclear membrane facilitates nuclear envelope biogenesis during mitosis
- PMID: 37398994
- PMCID: PMC10318406
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202208137
SUMOylation at the inner nuclear membrane facilitates nuclear envelope biogenesis during mitosis
Abstract
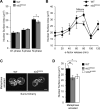
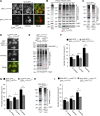
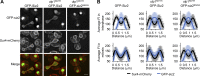
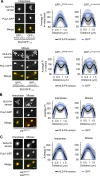
As eukaryotic cells progress through cell division, the nuclear envelope (NE) membrane must expand to accommodate the formation of progeny nuclei. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, closed mitosis allows visualization of NE biogenesis during mitosis. During this period, the SUMO E3 ligase Siz2 binds the inner nuclear membrane (INM) and initiates a wave of INM protein SUMOylation. Here, we show these events increase INM levels of phosphatidic acid (PA), an intermediate of phospholipid biogenesis, and are necessary for normal mitotic NE membrane expansion. The increase in INM PA is driven by the Siz2-mediated inhibition of the PA phosphatase Pah1. During mitosis, this results from the binding of Siz2 to the INM and dissociation of Spo7 and Nem1, a complex required for the activation of Pah1. As cells enter interphase, the process is then reversed by the deSUMOylase Ulp1. This work further establishes a central role for temporally controlled INM SUMOylation in coordinating processes, including membrane expansion, that regulate NE biogenesis during mitosis.
© 2023 Saik et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures






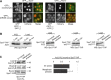
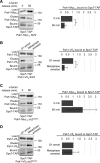
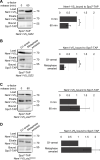

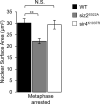
Comment in
-
Oiling the wheels of nuclear division: SUMOylation regulates the expansion of the mitotic nuclear membrane.J Cell Biol. 2023 Aug 7;222(8):e202306126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202306126. Epub 2023 Jul 13. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37440179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbosa, A.D., Lim K., Mari M., Edgar J.R., Gal L., Sterk P., Jenkins B.J., Koulman A., Savage D.B., Schuldiner M., et al. . 2019. Compartmentalized synthesis of triacylglycerol at the inner nuclear membrane regulates nuclear organization. Dev. Cell. 50:755–766.e6. 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.07.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brachmann, C.B., Davies A., Cost G.J., Caputo E., Li J., Hieter P., and Boeke J.D.. 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast. 14(2):115–132. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19980130)14:2<115::AID-YEA204>3.0.CO;2-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

