Budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles-1 (BUB1) regulates EGFR signaling by reducing EGFR internalization
- PMID: 37399454
- PMCID: PMC10373970
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204820
Budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles-1 (BUB1) regulates EGFR signaling by reducing EGFR internalization
Abstract
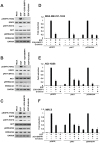
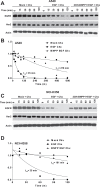
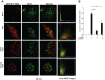
EGFR signaling initiates upon ligand binding which leads to activation and internalization of the receptor-ligand complex. Here, we evaluated if BUB1 impacted EGFR signaling by regulating EGFR receptor internalization and activation. BUB1 was ablated genomically (siRNA) or biochemically (2OH-BNPP1) in cells. EGF ligand was used to initiate EGFR signaling while disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) was used for cross linking cellular proteins. EGFR signaling was measured by western immunoblotting and receptor internalization was evaluated by fluorescent microscopy (pEGFR (pY1068) colocalization with early endosome marker EEA1). siRNA mediated BUB1 depletion led to an overall increase in total EGFR levels and more phospho-EGFR (Y845, Y1092, and Y1173) dimers while the amount of total EGFR (non-phospho) dimers remained unchanged. BUB1 inhibitor (BUB1i) decreased EGF mediated EGFR signaling including pEGFR Y845, pAKT S473 and pERK1/2 in a time dependent manner. Additionally, BUB1i also reduced EGF mediated pEGFR (Y845) dimers (asymmetric dimers) without affecting total EGFR dimers (symmetric dimers) indicating that dimerization of inactive EGFR is not affected by BUB1. Furthermore, BUB1i blocked EGF mediated EGFR degradation (increase in EGFR half-life) without impacting half-lives of HER2 or c-MET. BUB1i also reduced co-localization of pEGFR with EEA1 positive endosomes suggesting that BUB1 might modulate EGFR endocytosis. Our data provide evidence that BUB1 protein and its kinase activity may regulate EGFR activation, endocytosis, degradation, and downstream signaling without affecting other members of the receptor tyrosine kinase family.
Keywords: BUB1; EGFR; cancer; endocytosis; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

