Discovery of VH domains that allosterically inhibit ENPP1
- PMID: 37400538
- PMCID: PMC10746542
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-023-01368-5
Discovery of VH domains that allosterically inhibit ENPP1
Abstract
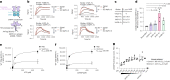
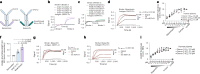
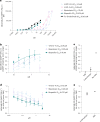
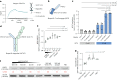
Ectodomain phosphatase/phosphodiesterase-1 (ENPP1) is overexpressed on cancer cells and functions as an innate immune checkpoint by hydrolyzing extracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP). Biologic inhibitors have not yet been reported and could have substantial therapeutic advantages over current small molecules because they can be recombinantly engineered into multifunctional formats and immunotherapies. Here we used phage and yeast display coupled with in cellulo evolution to generate variable heavy (VH) single-domain antibodies against ENPP1 and discovered a VH domain that allosterically inhibited the hydrolysis of cGAMP and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). We solved a 3.2 Å-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure for the VH inhibitor complexed with ENPP1 that confirmed its new allosteric binding pose. Finally, we engineered the VH domain into multispecific formats and immunotherapies, including a bispecific fusion with an anti-PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor that showed potent cellular activity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.E.S., J.A.W. and E.A.S.C. and the Reagents of the University of California have filed a provisional patent application related to this project.
Figures


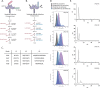
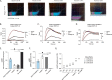
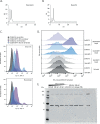
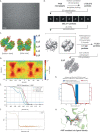
References
-
- Li J, et al. Metastasis and immune evasion from extracellular cGAMP hydrolysis. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:1212–1227. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0387. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

