Roles of hypoxic environment and M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles on the progression of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 37400770
- PMCID: PMC10318818
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-023-02468-7
Roles of hypoxic environment and M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles on the progression of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia contributes to the development of invasive and metastatic cancer cells, and is detrimental to cancer treatment. This study aimed to explore the molecular mechanisms by which hypoxic microenvironments affect hypoxic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) development and the effects of M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) on NSCLC cells.
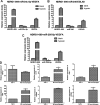
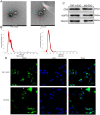
Methods: A549 cells were cultured in an anoxic incubator for 48 h to construct hypoxic A549 cells, and then normal and hypoxic A549 cells were harvested for RNA sequencing. Next, THP-1 cells were used to induce M2 macrophages, and EVs were isolated from THP-1 cells and M2 macrophages. Cell counting kit-8 and transwell assays were used to determine the viability and migration of hypoxic A549 cells, respectively.
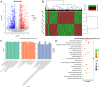
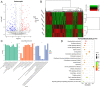
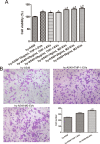
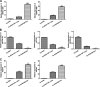
Results: After sequencing, 2426 DElncRNAs and 501 DEmiRNAs were identified in normal A549 cells and hypoxic A549 cells. These DElncRNAs and DEmiRNAs were significantly enriched in "Wnt signaling pathway," "Hippo signaling pathway," "Rap1 signaling pathway," "calcium signaling pathway," "mTOR signaling pathway," and "TNF signaling pathway." Subsequently, ceRNA networks consisting of 4 lncRNA NDRG1 transcripts, 16 miRNAs and 221 target mRNAs were built, and the genes in the ceRNA networks were significantly associated with "Hippo signaling pathway" and "HIF-1 signaling pathway." EVs were successfully extracted from THP-1 cells and M2 macrophages, and M2 macrophage-derived EVs significantly enhanced the viability and migration of hypoxic A549 cells. Finally, M2 macrophage-derived EVs further upregulated the expression of NDRG1-009, NDRG1-006, VEGFA, and EGLN3, while downregulating miR-34c-5p, miR-346, and miR-205-5p in hypoxic A549 cells.
Conclusions: M2 macrophage-derived EVs may worsen the progression of NSCLC in a hypoxic microenvironment by regulating the NDRG1-009-miR-34c-5p-VEGFA, NDRG1-006-miR-346-EGLN3, NDRG1-009-miR-205-5p-VEGFA, and Hippo/HIF-1 signaling pathways.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Hypoxia; M2 macrophages; Non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles secreted by hypoxia pre-challenged mesenchymal stem cells promote non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and mobility as well as macrophage M2 polarization via miR-21-5p delivery.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 8;38(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1027-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30736829 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-packaged miR-181c-5p from epithelial ovarian cancer cells promotes M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via the KAT2B/HOXA10 axis.J Gene Med. 2022 Oct;24(10):e3446. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3446. Epub 2022 Sep 19. J Gene Med. 2022. PMID: 36027869
-
Hypoxic glioma-derived extracellular vesicles harboring MicroRNA-10b-5p enhance M2 polarization of macrophages to promote the development of glioma.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Nov;28(11):1733-1747. doi: 10.1111/cns.13905. Epub 2022 Sep 2. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 36052751 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of M1 Macrophages and Their Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2024 Aug 26;13(17):1428. doi: 10.3390/cells13171428. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Immunomodulatory Role of Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;14(16):4001. doi: 10.3390/cancers14164001. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA MEG3 acts as a suppressor in breast cancer by regulating miR-330/CNN1.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 17;16(2):1318-1335. doi: 10.18632/aging.205419. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38240701 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Breast Cancer Subtypes Based on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Related Genes and Analysis of Prognosis and Immune Microenvironment in Breast Cancer Patients.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241241484. doi: 10.1177/15330338241241484. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38725284 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome therapeutics for non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 30;24(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03544-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39478574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mining and evaluation of adverse event signals for capmatinib based on the FAERS database.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1417661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1417661. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39380910 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

