An empirical approach to the definition of the target margins in eye radiosurgery
- PMID: 37401002
- PMCID: PMC10402678
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13982
An empirical approach to the definition of the target margins in eye radiosurgery
Abstract
Introduction: A system for stabilizing and monitoring eye movements during LINAC-based photon beam one single fraction stereotactic radiotherapy was developed at our Institution. This study aimed to describe the feasibility and the efficacy of our noninvasive optical localization system that was developed, tested, and applied in 20 patients treated for uveal melanoma.
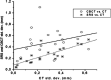
Methods: Our system consisted of a customized thermoplastic mask to immobilize the head, a gaze fixation LED, and a digital micro-camera. The localization procedure, which required the active collaboration of the patient, served to monitor the eye movements during all phases of the treatment, starting from the planning computed tomography up to the administration of radiotherapy, and allowed the operators to suspend the procedure and to interact with the patient in case of large movements of the pupil.
Results: Twenty patients were treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (27 Gy in one fraction) for primary uveal melanoma. All patients showed a good tolerance to the treatment; until now, all patients were in local control during the follow up and one died for distant progression 6 months after radiosurgery.
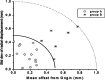
Conclusions: This study showed that this noninvasive technique, based on eye position control, is appropriate and can contribute to the success of LINAC-based stereotactic radiotherapy. A millimetric safety margin to the clinical target volume was adequate to take account for the organ movement. All patients treated till now showed a good local control; failures in the disease control were due to metastatic spread.
Keywords: CBCT; eye tracking; planning target volume; stereotactic radiosurgery; uveal melanoma.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- The Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study. (Accessed November 18, 2022). https://pages.jh.edu/wctb/coms/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

