Selective Collection of Exhaled Breath Condensate for Noninvasive Screening of Breath Glucose
- PMID: 37401788
- PMCID: PMC11688680
- DOI: 10.1177/19322968231179728
Selective Collection of Exhaled Breath Condensate for Noninvasive Screening of Breath Glucose
Abstract
Background: Although exhaled breath condensate (EBC) is a promising noninvasive sample for detecting respiratory analytes such as glucose, current EBC collection methods yield inconsistent results.
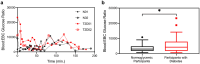
Methods: We developed a custom EBC collection device with a temperature-based algorithm to selectively condense alveolar air for reproducible EBC glucose detection. We characterized the condensate volumes and the corresponding glucose concentrations. We performed a pilot study demonstrating its use during oral glucose tolerance tests.
Results: The novel device selectively captured alveolar air resulting in slightly higher and less variable glucose concentrations than the overall EBC. Participants with type 2 diabetes demonstrated significantly higher blood plasma-EBC glucose ratios than normoglycemic participants.
Conclusions: Temperature-based selective EBC collection allows EBC glucose measurement and is a promising sampling method to distinguish patients with and without diabetes.
Keywords: exhaled breath condensate; glucose; point-of-care diagnostics; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: J.C.L. is a co-founder of OmniVis, Inc, EverTrue LLC, and Rescue Biomedical LLC, which have licensed Purdue University technology to develop point-of-care diagnostics and wearable monitoring technologies. At the time of publication, D.T. was an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb, Summit, NJ. All aspects of the study preceded and were independent of this employment. At the time of publication, K.M. was an employee of Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN. All aspects of the study preceded and were independent of this employment.
Figures

References
-
- Gupta S, Sandhu SV, Bansal H, Sharma D. Comparison of salivary and serum glucose levels in diabetic patients. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1932296814552673. Published 2014. Accessed April 9, 2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reim M, Lax F, Lichte H, Turss R. Steady state levels of glucose in the different layers of the cornea, aqueous humor, blood and tears in vivo. Ophthalmologica. 1967;154(1):39-50. https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/305147. Accessed April 9, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Optica Publishing Group. In vitro measurements of physiological glucose concentrations in biological fluids using mid-infrared light. https://www.osapublishing.org/boe/abstract.cfm?uri=boe-4-7-1083. Published 2013. Accessed April 9, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

