Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events by Baseline Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis Treated with Tofacitinib: Data from the OCTAVE Clinical Programme
- PMID: 37402275
- PMCID: PMC10673809
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad104
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events by Baseline Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis Treated with Tofacitinib: Data from the OCTAVE Clinical Programme
Abstract
Background and aims: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease have increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular [CV] disease [ASCVD]. Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis [UC]. We report major adverse CV events [MACE] in the UC OCTAVE programme, stratified by baseline CV risk.
Methods: Rates of MACE were analysed by baseline [first tofacitinib exposure] CV risk profile: prior ASCVD, or 10-year ASCVD risk categories [low, borderline, intermediate, high].
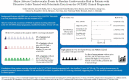
Results: Of 1157 patients [2814.4 patient-years of exposure; ≤7.8 years' tofacitinib treatment], 4% had prior ASCVD and 83% had no prior ASCVD and low-borderline baseline 10-year ASCVD risk. Eight [0.7%] patients developed MACE; one had prior ASCVD. Incidence rates [unique patients with events/100 patient-years of exposure; 95% confidence intervals] for MACE were: 0.95 [0.02-5.27] in patients with prior ASCVD; and 1.81 [0.05-10.07], 1.54 [0.42-3.95], 0.00 [0.00-2.85], and 0.09 [0.01-0.32] in patients without prior ASCVD and with high, intermediate, -borderline, and low baseline 10-year ASCVD risk, respectively. For the 5/7 patients with MACE and without prior ASCVD, 10-year ASCVD risk scores were numerically higher [>1%] prior to MACE versus at baseline, primarily due to increasing age.
Conclusions: Most patients receiving tofacitinib in the UC OCTAVE programme had low baseline 10-year ASCVD risk. MACE were more frequent in patients with prior ASCVD and higher baseline CV risk. This analysis demonstrates potential associations between baseline CV risk and MACE in patients with UC, suggesting CV risk should be assessed individually in clinical practice.
Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00787202; NCT01465763; NCT01458951; NCT01458574; NCT01470612.
Keywords: Ulcerative colitis; cardiovascular risk; inflammatory bowel disease.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Conflict of interest statement
SS has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Arena, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Dr Falk Pharma, Eli Lilly, Ferring, Fresenius, Galapagos, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, I-MAB Biopharma, Janssen, Merck, Novartis/Sandoz, Pfizer Inc, Protagonist, Takeda, and Theravance. DTR has received consulting fees from AbbVie, AltruBio, Arena, Bellatrix Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corp/Syneos, Connect BioPharma, Eli Lilly, GalenPharma/Atlantica, Genentech/Roche, Gilead Sciences, InDex Pharmaceuticals, Iterative Scopes, Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Prometheus Biosciences, Reistone, Takeda, and Techlab; and research support from Takeda. SCN has received research support from AbbVie, Ferring, and Olympus; speaker fees from AbbVie, Ferring, Janssen, Menarini, Pfizer Inc, Takeda, and Tillotts; and holds a directorship with Microbiota I-Center. LP-B has received personal fees from AbbVie, Alimentiv, Allergan, Amgen, Arena, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Enthera, Ferring, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Gossamer Bio, InDex Pharmaceuticals, Inotrem, Janssen, MSD, Mylan, Norgine, ONO Pharma, OSE Immunotherapeutics, Pandion Therapeutics, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, Takeda, Theravance, Thermo Fisher, Tillotts, Viatris, and Vifor Pharma; research support from AbbVie, Fresenius Kabi, MSD, and Takeda; and holds stock options for CTMA. SD has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Allergan, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, Ferring, Gilead Sciences, Hospira, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Mundipharma, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Sandoz, Takeda, TiGenix, UCB, and Vifor Pharma. IM, XG, CS, KKK, YC, and AY are employees and shareholders of Pfizer Inc. HJ is a former employee of Syneos Health, which was a paid contractor to Pfizer Inc in connection with the development of this manuscript and related statistical analysis. WR has received research support from AbbVie, Janssen, MSD, Sandoz, Sanofi, and Takeda; lecture fees from AbbVie, Celltrion, Dr Falk Pharma, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer Inc, Pharmacosmos, Roche, Shire, Takeda, and Therakos; consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AM Pharma, AOP Orphan, Arena, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bioclinica, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Calyx, Celgene, Cellerix, Dr Falk Pharma, Eli Lilly, Ferring, Galapagos, Gatehouse Bio Inc, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Grünenthal, ICON, InDex Pharmaceuticals, iNova, Janssen, Landos Biopharma, Medahead, MedImmune, Microbiotica, Millennium, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Novartis, OMass, Otsuka, Parexel, Periconsulting, Pfizer Inc, Pharmacosmos, Protagonist, Provention, Quell Therapeutics, Sandoz, Seres Therapeutics, SetPoint Medical, Sigmoid, Sublimity, Takeda, Teva Pharma, Therakos, Theravance, and Zealand; and advisory board fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Galapagos, Janssen, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Pfizer Inc, Pharmacosmos, Sandoz, and Takeda. MCD has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Prometheus Laboratories, Takeda, and UCB.
Figures


References
-
- Sandborn WJ, Ghosh S, Panes J, et al.; Study A3921062 Investigators. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in active ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 2012;367:616–24. - PubMed
-
- Sandborn WJ, Su C, Sands BE, et al.; OCTAVE Induction 1, OCTAVE Induction 2, and OCTAVE Sustain Investigators. Tofacitinib as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1723–36. - PubMed
-
- Cainzos-Achirica M, Glassner K, Zawahir HS, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:2895–905. - PubMed

