The brain-gut-microbiota axis in the treatment of neurologic and psychiatric disorders
- PMID: 37402401
- PMCID: PMC10371417
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1767818
The brain-gut-microbiota axis in the treatment of neurologic and psychiatric disorders
Abstract
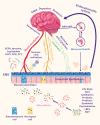
The human gut microbiota is a complex ecosystem made of trillions of microorganisms. The composition can be affected by diet, metabolism, age, geography, stress, seasons, temperature, sleep, and medications. The increasing evidence about the existence of a close and bi-directional correlation between the gut microbiota and the brain indicates that intestinal imbalance may play a vital role in the development, function, and disorders of the central nervous system. The mechanisms of interaction between the gut-microbiota on neuronal activity are widely discussed. Several potential pathways are involved with the brain-gut-microbiota axis, including the vagus nerve, endocrine, immune, and biochemical pathways. Gut dysbiosis has been linked to neurological disorders in different ways that involve activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, imbalance in neurotransmitter release, systemic inflammation, and increase in the permeability of the intestinal and the blood-brain barrier. Mental and neurological diseases have become more prevalent during the coronavirus disease 2019pandemic and are an essential issue in public health globally. Understanding the importance of diagnosing, preventing, and treating dysbiosis is critical because gut microbial imbalance is a significant risk factor for these disorders. This review summarizes evidence demonstrating the influence of gut dysbiosis on mental and neurological disorders.
A microbiota intestinal humana é um ecossistema complexo feito de trilhões de microrganismos, cuja composição pode ser afetada pela dieta, pelo metabolismo, pela idade, geografia, pelo estresse, pelas estações do ano, pela temperatura, pelo sono e por medicamentos. A crescente evidência sobre a existência de uma correlação estreita e bidirecional entre a microbiota intestinal e o cérebro indica que o desequilíbrio intestinal pode desempenhar um papel vital no desenvolvimento, na função e nos distúrbios do sistema nervoso central. Os mecanismos de interação entre a microbiota intestinal e a atividade neuronal são amplamente discutidos. Várias vias potenciais estão envolvidas com o eixo microbiota-intestino-cérebro, incluindo o nervo vago e as vias endócrinas, imunes e bioquímicas. A disbiose intestinal tem sido associada a distúrbios neurológicos de diferentes maneiras que envolvem a ativação do eixo hipotálamo-hipófise-adrenal, o desequilíbrio na liberação de neurotransmissores, a inflamação sistêmica e o aumento da permeabilidade das barreiras intestinal e hematoencefálica. As doenças mentais e neurológicas tornaram-se mais prevalentes durante a pandemia de coronavirus disease 2019 e são uma questão global essencial na saúde pública. Compreender a importância de diagnosticar, prevenir e tratar a disbiose é fundamental porque o desequilíbrio microbiano intestinal é um fator de risco significativo para esses distúrbios. Esta revisão resume as evidências que demonstram a influência da disbiose intestinal em distúrbios mentais e neurológicos.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical