Senolysis through thrombomodulation
- PMID: 37402898
- PMCID: PMC10397178
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-023-00842-y
Senolysis through thrombomodulation
Figures
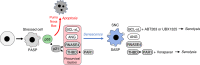
Comment on
-
Antagonizing the irreversible thrombomodulin-initiated proteolytic signaling alleviates age-related liver fibrosis via senescent cell killing.Cell Res. 2023 Jul;33(7):516-532. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00820-4. Epub 2023 May 11. Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 37169907 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

