Towards an Implementation-STakeholder Engagement Model (I-STEM) for improving health and social care services
- PMID: 37403248
- PMCID: PMC10485327
- DOI: 10.1111/hex.13808
Towards an Implementation-STakeholder Engagement Model (I-STEM) for improving health and social care services
Abstract
Background: The implementation science literature acknowledges a need for engagement of key stakeholders when designing, delivering and evaluating implementation work. To date, the literature reports minimal or focused stakeholder engagement, where stakeholders are engaged in either barrier identification and/or barrier prioritisation. This paper begins to answer calls from the literature for the development of tools and guidance to support comprehensive stakeholder engagement in implementation research and practice. The paper describes the systematic development of the Implementation-STakeholder Engagement Model (I-STEM) in the context of an international, large-scale empirical implementation study (ImpleMentAll) aimed at evaluating the effectiveness of a tailored implementation toolkit. The I-STEM is a sensitising tool that defines key considerations and activities for undertaking stakeholder engagement activities across an implementation process.
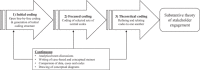
Methods: In-depth, semistructured interviews and observations were conducted with implementers who were tailoring implementation strategies to integrate and embed internet-based cognitive behavioural therapy (iCBT) services in 12 routine mental health care organisations in nine countries in Europe and Australia. The analytical process was informed by principles of first- and third-generation Grounded Theory, including constant comparative method.
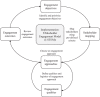
Results: We conducted 55 interviews and observed 19 implementation-related activities (e.g., team meetings and technical support calls). The final outcome of our analysis is expressed in an initial version of the I-STEM, consisting of five interrelated concepts: engagement objectives, stakeholder mapping, engagement approaches, engagement qualities and engagement outcomes. Engagement objectives are goals that implementers plan to achieve by working with stakeholders in the implementation process. Stakeholder mapping involves identifying a range of organisations, groups or people who may be instrumental in achieving the engagement objectives. Engagement approaches define the type of work that is undertaken with stakeholders to achieve the engagement objectives. Engagement qualities define the logistics of the engagement approach. Lastly, every engagement activity may result in a range of engagement outcomes.
Conclusion: The I-STEM represents potential avenues for substantial stakeholder engagement activity across key phases of an implementation process. It provides a conceptual model for the planning, delivery, evaluation and reporting of stakeholder engagement activities. The I-STEM is nonprescriptive and highlights the importance of a flexible, iterative approach to stakeholder engagement. It is developmental and will require application and validation across a range of implementation activities.
Patient or public contribution: Patient contribution to ImpleMentAll trial was facilitated by GAMIAN-Europe at all stages-from grant development to dissemination. GAMIAN-Europe brings together a wide variety of patient representation organisations (local, regional and national) from almost all European countries. GAMIAN-Europe was involved in pilot testing the ItFits-toolkit and provided their views on the various aspects, including stakeholder engagement. Patients were also represented in the external advisory board providing support and advice on the design, conduct and interpretation of the wider project, including the development of the ItFits-toolkit.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03652883. Retrospectively registered on 29 August 2018.
Keywords: co-design; co-production; implementation strategies; normalisation; stakeholder engagement; tailored implementation.
© 2023 The Authors. Health Expectations published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Carrozza C. Democratizing expertise and environmental governance: different approaches to the politics of science and their relevance for policy analysis. J Environ Policy Plan. 2015;17(1):108‐126.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

