Large-Scale Data Harmonization Across Prospective Studies
- PMID: 37403415
- PMCID: PMC10988223
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwad153
Large-Scale Data Harmonization Across Prospective Studies
Abstract
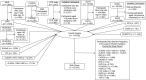
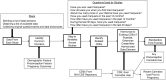
The Preconception Period Analysis of Risks and Exposures Influencing Health and Development (PrePARED) Consortium creates a novel resource for addressing preconception health by merging data from numerous cohort studies. In this paper, we describe our data harmonization methods and results. Individual-level data from 12 prospective studies were pooled. The crosswalk-cataloging-harmonization procedure was used. The index pregnancy was defined as the first postbaseline pregnancy lasting more than 20 weeks. We assessed heterogeneity across studies by comparing preconception characteristics in different types of studies. The pooled data set included 114,762 women, and 25,531 (22%) reported at least 1 pregnancy of more than 20 weeks' gestation during the study period. Babies from the index pregnancies were delivered between 1976 and 2021 (median, 2008), at a mean maternal age of 29.7 (standard deviation, 4.6) years. Before the index pregnancy, 60% of women were nulligravid, 58% had a college degree or more, and 37% were overweight or obese. Other harmonized variables included race/ethnicity, household income, substance use, chronic conditions, and perinatal outcomes. Participants from pregnancy-planning studies had more education and were healthier. The prevalence of preexisting medical conditions did not vary substantially based on whether studies relied on self-reported data. Use of harmonized data presents opportunities to study uncommon preconception risk factors and pregnancy-related events. This harmonization effort laid the groundwork for future analyses and additional data harmonization.
Keywords: consortia; data harmonization; preconception period; pregnancy; pregnancy complications.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 2023.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen JM, Cesta CE, Kjerpeseth L, et al. A common data model for harmonization in the Nordic Pregnancy Drug Safety Studies (NorPreSS). Norsk Epidemiologi. 2021;29(1-2):117–123.
-
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development . Promoting Data Harmonization to Accelerate COVID-19 Pregnancy Research . Bethesda, MD: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2021. https://www.niehs.nih.gov/research/programs/disaster/database/promoting_.... Accessed April 10, 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 HD072326/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL145386/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD032194/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016592/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD001479/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD094322/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD086742/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL015103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121230/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 ES028521/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041200/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK059944/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020488/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD105863/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES029951/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD069587/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES028923/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800006I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

