Echinacoside-Zinc Nanomaterial Inhibits Skin Glycation by Suppressing the Transcriptional Activation of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products
- PMID: 37403876
- PMCID: PMC10373517
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c04726
Echinacoside-Zinc Nanomaterial Inhibits Skin Glycation by Suppressing the Transcriptional Activation of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products
Abstract
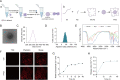
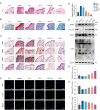
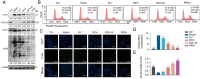
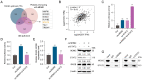
Glycation is a nonenzymatically catalyzed spontaneous reaction that eventually leads to the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which can bind to the receptor for AGEs (RAGE). The consequences are oxidative damage, an inflammatory response, and aging. In this work, we synthesized echinacoside-zinc coordination polymers (ECH-Zn) by using the coordination interaction between the catechol group of ECH and zinc ions. ECH-Zn was further wrapped with hyaluronic acid/poly (ethylenimine) (HA-PEI) to obtain spherical nanoparticle polymers of HA-PEI-coated ECH-Zn (PPZn). PPZn can enhance the uptake and utilization of ECH-Zn and also have a better antiglycation effect in the skin under the effect of promoting transdermal absorption of HA-PEI. Mechanistic studies at the cellular level showed that MDM2 can interact with STAT2 to form a transcriptional complex and thus promote RAGE transcriptional activation. In vitro and in vivo studies revealed that PPZn can decrease the expression and inhibit the interaction of the MDM2/STAT2 complex. It inhibited the function of the MDM2/STAT2 complex and suppressed the transcriptional activation of RAGE, thereby exerting antiglycation effects. In conclusion, this work provides a nanomaterial and elucidated a mechanism of anti-skin glycation.
Keywords: MDM2; RAGE; STAT2; echinacoside; glycation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pageon H.; Zucchi H.; Pennacchi P. C.; Asselineau D.. Glycation and Skin Aging. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage M. A.; Miller K. W.; Maibach H. I., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2017; pp 1247–1270.
-
- Gomes R. A.; Oliveira L. M.; Silva M.; Ascenso C.; Quintas A.; Costa G.; Coelho A. V.; Sousa Silva M.; Ferreira A. E.; Ponces Freire A.; et al. Protein glycation in vivo: functional and structural effects on yeast enolase. Biochemical journal 2008, 416 (3), 317–326. 10.1042/bj20080632. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

