Assisted reproductive techniques do not impact late neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm children
- PMID: 37404562
- PMCID: PMC10315460
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1123183
Assisted reproductive techniques do not impact late neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm children
Abstract
Objective: Assisted reproductive technology (ART) increases the rate of preterm births, though few studies have analyzed outcomes for these infants. No data are available on 4-year-old children born prematurely after ART. The objective was to investigate whether ART affect the neurodevelopmental outcomes at 4 years in preterm infants born before 34 weeks of gestational age (GA).
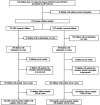
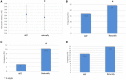
Methods and results: A total of 166 ART and 679 naturally conceived preterm infants born before 34 weeks GA between 2013 and 2015 enrolled in the Loire Infant Follow-up Team were included. Neurodevelopment was assessed at 4 years using the age and stage questionnaire (ASQ) and the need for therapy services. The association between the socio-economic and perinatal characteristics and non-optimal neurodevelopment at 4 years was estimated. After adjustment, the ART preterm group remained significantly associated with a lower risk of having at least two domains in difficulty at ASQ: adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 0.34, 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.13-0.88), p = 0.027. The factors independently associated with non-optimal neurodevelopment at 4 years were male gender, low socio-economic level, and 25-30 weeks of GA at birth. The need for therapy services was similar between groups (p = 0.079). The long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm children born after ART are very similar, or even better than that of the spontaneously conceived children.
Keywords: assisted reproductive technology; cognitive development; follow-up; in vitro fertilization; prematurity.
© 2023 Lefebvre, Flamant, Olivier, Gascoin, Bouet, Roze, Barrière, Fréour and Muller.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blencowe H, Cousens S, Oestergaard MZ, Chou D, Moller A-B, Narwal R, et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of preterm birth rates in the year 2010 with time trends since 1990 for selected countries: a systematic analysis and implications. Lancet. (2012) 379(9832):2162–72. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60820-4 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

