Functional role of MicroRNA/PI3K/AKT axis in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 37404761
- PMCID: PMC10315918
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1219211
Functional role of MicroRNA/PI3K/AKT axis in osteosarcoma
Abstract
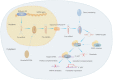
Osteosarcoma (OS) is a primary malignant bone tumor that occurs in children and adolescents, and the PI3K/AKT pathway is overactivated in most OS patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are highly conserved endogenous non-protein-coding RNAs that can regulate gene expression by repressing mRNA translation or degrading mRNA. MiRNAs are enriched in the PI3K/AKT pathway, and aberrant PI3K/AKT pathway activation is involved in the development of osteosarcoma. There is increasing evidence that miRNAs can regulate the biological functions of cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. MiRNA/PI3K/AKT axis can regulate the expression of osteosarcoma-related genes and then regulate cancer progression. MiRNA expression associated with PI3K/AKT pathway is also clearly associated with many clinical features. In addition, PI3K/AKT pathway-associated miRNAs are potential biomarkers for osteosarcoma diagnosis, treatment and prognostic assessment. This article reviews recent research advances on the role and clinical application of PI3K/AKT pathway and miRNA/PI3K/AKT axis in the development of osteosarcoma.
Keywords: MicroRNA; PI3K/AKT pathway; biomarker; mechanism; osteosarcoma.
Copyright © 2023 Xiang, Yang, Liu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detailed role of microRNA-mediated regulation of PI3K/AKT axis in human tumors.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Jan;42(1):e3904. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3904. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38102946 Review.
-
LncRNA FER1L4 induces apoptosis and suppresses EMT and the activation of PI3K/AKT pathway in osteosarcoma cells via inhibiting miR-18a-5p to promote SOCS5.Gene. 2019 Dec 30;721:144093. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144093. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31473323
-
Exosomal microRNA as a key regulator of PI3K/AKT pathways in human tumors.Med Oncol. 2024 Oct 14;41(11):265. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02529-9. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39400677 Review.
-
MicroRNA‑22 mediates the cisplatin resistance of osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Oncol Rep. 2020 Apr;43(4):1169-1186. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7492. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32323781 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-196a overexpression promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis through PTEN/Akt/FOXO1 pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):2461-72. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045752 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
circSLC39A8 by sponging hsa-miR-11181-5p and direct binding to PIK3CA mRNA promotes retinoblastoma proliferation.J Cancer. 2025 Apr 21;16(8):2434-2448. doi: 10.7150/jca.99599. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40535798 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs and regulation of the PI3K signaling pathway in lung cancer: Recent insights and potential clinical applications.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Dec 3;11:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.11.006. eCollection 2025 Apr. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39720352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DDTC-Cu(I) inhibits human osteosarcoma cells growth by repressing MET/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21780. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06748-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594499 Free PMC article.
-
Urolithin A suppressed osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion via targeting MMPs and AKT1.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 17;15(1):25941. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11804-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40676084 Free PMC article.
-
Vitexicarpin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastatic Properties via the AKT-PRAS40 Pathway in Human Osteosarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 22;25(7):3582. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073582. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612399 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

