Tocilizumab (monoclonal anti-IL-6R antibody) reverses anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 37404767
- PMCID: PMC10315670
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1192472
Tocilizumab (monoclonal anti-IL-6R antibody) reverses anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma
Abstract
Purpose: Anlotinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) has been in clinical application to inhibit malignant cell growth and lung metastasis in osteosarcoma (OS). However, a variety of drug resistance phenomena have been observed in the treatment. We aim to explore the new target to reverse anlotinib resistance in OS.
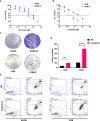
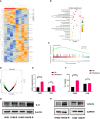
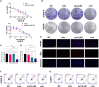
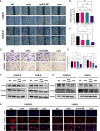
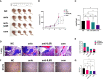
Materials and methods: In this study, we established four OS anlotinib-resistant cell lines, and RNA-sequence was performed to evaluate differentially expressed genes. We verified the results of RNA-sequence by PCR, western blot and ELISA assay. We further explored the effects of tocilizumab (anti- IL-6 receptor), either alone or in combined with anlotinib, on the inhibition of anlotinib-resistant OS cells malignant viability by CCK8, EDU, colony formation, apoptosis, transwell, wound healing, Cytoskeletal stain assays, and xenograft nude mouse model. The expression of IL-6 in 104 osteosarcoma samples was tested by IHC.
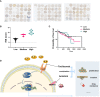
Results: We found IL-6 and its downstream pathway STAT3 were activated in anlotinib-resistant osteosarcoma. Tocilizumab impaired the tumor progression of anlotinib-resistant OS cells, and combined treatment with anlotinib augmented these effects by inhibiting STAT3 expressions. IL-6 was highly expressed in patients with OS and correlated with poor prognosis.
Conclusion: Tocilizumab could reverse anlotinib resistance in OS by IL-6/STAT3 pathway and the combination treatment with anlotinib rationalized further studies and clinical treatment of OS.
Keywords: anlotinib; drug resistance; interleukin-6; osteosarcoma; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Chen, Sun, Shi, Wang, Huang, Ren and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

