Alternatives to antibiotics for treatment of mastitis in dairy cows
- PMID: 37404775
- PMCID: PMC10315858
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1160350
Alternatives to antibiotics for treatment of mastitis in dairy cows
Abstract
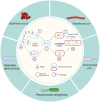
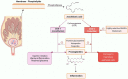
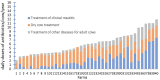
Mastitis is considered the costliest disease on dairy farms and also adversely affects animal welfare. As treatment (and to a lesser extent prevention) of mastitis rely heavily on antibiotics, there are increasing concerns in veterinary and human medicine regarding development of antimicrobial resistance. Furthermore, with genes conferring resistance being capable of transfer to heterologous strains, reducing resistance in strains of animal origin should have positive impacts on humans. This article briefly reviews potential roles of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), herbal medicines, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), bacteriophages and their lytic enzymes, vaccination and other emerging therapies for prevention and treatment of mastitis in dairy cows. Although many of these approaches currently lack proven therapeutic efficacy, at least some may gradually replace antibiotics, especially as drug-resistant bacteria are proliferating globally.
Keywords: NSAIDs; antimicrobial peptides; bacteriophages; bovine mastitis; dairy cows; herbal medicines; vaccination.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Xu, Liang, Kastelic, Han, Tong and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial resistance of mastitis pathogens.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2012 Jul;28(2):165-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2012.03.005. Epub 2012 Apr 28. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2012. PMID: 22664201 Review.
-
Impact of antibiotic use in adult dairy cows on antimicrobial resistance of veterinary and human pathogens: a comprehensive review.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2011 Mar;8(3):337-55. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2010.0730. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2011. PMID: 21133795 Review.
-
An Update on the Effect of Clinical Mastitis on the Welfare of Dairy Cows and Potential Therapies.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2018 Nov;34(3):525-535. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2018.07.006. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2018. PMID: 30316508 Review.
-
Prevalence of Mastitis and Phenotypic Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Lactating Dairy Cows of Selected Dairy Farms in and Around Adama Town, Central Ethiopia.Environ Health Insights. 2021 May 28;15:11786302211021297. doi: 10.1177/11786302211021297. eCollection 2021. Environ Health Insights. 2021. PMID: 34103935 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine mastitis prevention and control in the post-antibiotic era.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021 Mar 31;53(2):236. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02680-9. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021. PMID: 33788033 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, multidrug-resistant S. aureus, and Enterococcus faecium-causing mastitis in Thailand and Cambodia.Vet World. 2025 Jan;18(1):202-209. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2025.202-209. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Vet World. 2025. PMID: 40041509 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-Derived Endolysins Against Resistant Staphylococcus spp.: A Review of Features, Antibacterial Activities, and Recent Applications.Infect Dis Ther. 2025 Jan;14(1):13-57. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-01069-z. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Infect Dis Ther. 2025. PMID: 39549153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Cloxacillin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Against Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms in Subclinical Mastitis.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Jan 3;82(2):65. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-04030-y. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39753774
-
Antimicrobial therapy approaches in the mastitis control driven by one health insights.Braz J Vet Med. 2024 Jul 17;46:e002624. doi: 10.29374/2527-2179.bjvm002624. eCollection 2024. Braz J Vet Med. 2024. PMID: 39104804 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Bovine Mastitis: Application of Metabolomics in Screening Its Predictive and Diagnostic Biomarkers.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 4;14(15):2264. doi: 10.3390/ani14152264. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Korhonen HJ, Marnila P. 10 - Bovine milk immunoglobulins against microbial human diseases. In: Dairy-Derived Ingredients. ed. Corredig M. (Sawston: Woodhead Publishing; ). (2009), 269–89.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

