Porphyromonas gingivalis induces an inflammatory response via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in a periodontitis mouse model
- PMID: 37405166
- PMCID: PMC10315844
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1183415
Porphyromonas gingivalis induces an inflammatory response via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in a periodontitis mouse model
Abstract
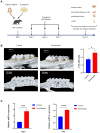
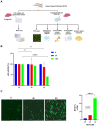
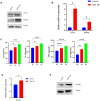
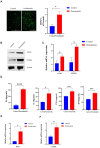
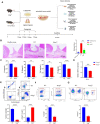
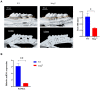
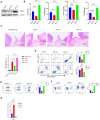
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease initiated by periodontopathogenic bacteria in the dental plaque biofilms. Understanding the role of Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis), a keystone pathogen associated with chronic periodontitis, in the inflammatory response is crucial. Herein, we investigated whether P. gingivalis infection triggers the expression of the type I IFN gene and various cytokines and leads to activation of the cGAMP synthase-stimulator of IFN genes (cGAS-STING) pathway both in vitro and in a mouse model. Additionally, in an experimental model of periodontitis using P. gingivalis, StingGt mice showed lower levels of inflammatory cytokines and bone resorption than wild-type mice. Furthermore, we report that a STING inhibitor (SN-011) significantly decreased inflammatory cytokine production and osteoclast formation in a periodontitis mouse model with P. gingivalis. In addition, STING agonist (SR-717) -treated periodontitis mice displayed enhanced macrophage infiltration and M1 macrophage polarization in periodontal lesions compared with that in vehicle-treated periodontitis mice. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that the cGAS-STING signaling pathway may be one of the key mechanisms crucial for the P. gingivalis-induced inflammatory response that leads to chronic periodontitis.
Keywords: Porphyromonas gingivalis; RANKL; cGAS-STING signaling pathway; macrophage polarization; osteoclast; periodontal disease; proinflammatory cytokines.
Copyright © 2023 Bi, Yang, Liao, Ji, Ma, Cai, Li, Yang, Sun, Liang and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

