Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence using cone-beam computed tomography imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region: A scoping review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37405196
- PMCID: PMC10315225
- DOI: 10.5624/isd.20220224
Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence using cone-beam computed tomography imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region: A scoping review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to conduct a scoping review and meta-analysis to provide overall estimates of the recall and precision of artificial intelligence for detection and segmentation using oral and maxillofacial cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
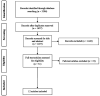
Materials and methods: A literature search was done in Embase, PubMed, and Scopus through October 31, 2022 to identify studies that reported the recall and precision values of artificial intelligence systems using oral and maxillofacial CBCT images for the automatic detection or segmentation of anatomical landmarks or pathological lesions. Recall (sensitivity) indicates the percentage of certain structures that are correctly detected. Precision (positive predictive value) indicates the percentage of accurately identified structures out of all detected structures. The performance values were extracted and pooled, and the estimates were presented with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
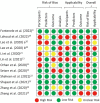
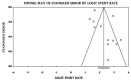
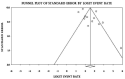
Results: In total, 12 eligible studies were finally included. The overall pooled recall for artificial intelligence was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.87-0.94). In a subgroup analysis, the pooled recall was 0.88 (95% CI: 0.77-0.94) for detection and 0.92 (95% CI: 0.87-0.96) for segmentation. The overall pooled precision for artificial intelligence was 0.93 (95% CI: 0.88-0.95). A subgroup analysis showed that the pooled precision value was 0.90 (95% CI: 0.77-0.96) for detection and 0.94 (95% CI: 0.89-0.97) for segmentation.
Conclusion: Excellent performance was found for artificial intelligence using oral and maxillofacial CBCT images.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Cone-Beam Computed Tomography; Dentistry; Predictive Value of Tests.
Copyright © 2023 by Korean Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None
Figures




References
-
- Signorelli L, Patcas R, Peltomäki T, Schätzle M. Radiation dose of cone-beam computed tomography compared to conventional radiographs in orthodontics. J Orofac Orthop. 2016;77:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Barnett CW, Glickman GN, Umorin M, Jalali P. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of cone-beam computed tomography in identification of apical periodontitis. J Endod. 2018;44:938–940. - PubMed
-
- Parker JM, Mol A, Rivera EM, Tawil PZ. Cone-beam computed tomography uses in clinical endodontics: observer variability in detecting periapical lesions. J Endod. 2017;43:184–187. - PubMed

