Psoriasis immunometabolism: progress on metabolic biomarkers and targeted therapy
- PMID: 37405259
- PMCID: PMC10317015
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1201912
Psoriasis immunometabolism: progress on metabolic biomarkers and targeted therapy
Abstract
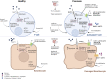
Psoriasis is a common inflammatory disease that affects mainly the skin. However, the moderate to severe forms have been associated with several comorbidities, such as psoriatic arthritis, Crohn's disease, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Keratinocytes and T helper cells are the dominant cell types involved in psoriasis development via a complex crosstalk between epithelial cells, peripheral immune cells and immune cells residing in the skin. Immunometabolism has emerged as a potent mechanism elucidating the aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis, offering novel specific targets to diagnose and treat psoriasis early. The present article discusses the metabolic reprogramming of activated T cells, tissue-resident memory T cells and keratinocytes in psoriatic skin, presenting associated metabolic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. In psoriatic phenotype, keratinocytes and activated T cells are glycolysis dependent and are characterized by disruptions in the TCA cycle, the amino acid metabolism and the fatty acid metabolism. Upregulation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) results in hyperproliferation and cytokine secretion by immune cells and keratinocytes. Metabolic reprogramming through the inhibition of affected metabolic pathways and the dietary restoration of metabolic imbalances may thus present a potent therapeutic opportunity to achieve long-term management of psoriasis and improved quality of life with minimum adverse effects.
Keywords: T cell; TCA; biomarkers; glycolysis; keratinocyte; lipid metabolism; metabolic targets; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2023 Sarandi, Krueger-Krasagakis, Tsoukalas, Sidiropoulou, Evangelou, Sifaki, Rudofsky, Drakoulis and Tsatsakis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

