Incarceration of Youths in an Adult Correctional Facility and Risk of Premature Death
- PMID: 37405770
- PMCID: PMC10323704
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.21805
Incarceration of Youths in an Adult Correctional Facility and Risk of Premature Death
Erratum in
-
Error in Wording.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2326692. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26692. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37486636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Youths incarcerated in adult correctional facilities are exposed to a variety of adverse circumstances that could diminish psychological and physical health, potentially leading to early mortality.
Objective: To evaluate whether being incarcerated in an adult correctional facility as a youth was associated with mortality between 18 and 39 years of age.
Design, setting, and participants: This cohort study relied on longitudinal data collected from 1997 to 2019 as part of the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth-1997, a nationally representative sample of 8984 individuals born in the United States between January 1, 1980, and December 1, 1984. The data analyzed for the current study were derived from annual interviews between 1997 and 2011 and interviews every other year from 2013 to 2019 (19 interviews in total). Participants were limited to respondents aged 17 years or younger during the 1997 interview and alive during their 18th birthday (8951 individuals; >99% of the original sample). Statistical analysis was performed from November 2022 to May 2023.
Intervention: Incarceration in an adult correctional facility before the age of 18 years compared with being arrested before the age of 18 years or never arrested or incarcerated before the age of 18 years.
Main outcomes and measures: The main outcome for the study was age at mortality between 18 and 39 years of age.
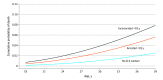
Results: The sample of 8951 individuals included 4582 male participants (51%), 61 American Indian or Alaska Native participants (1%), 157 Asian participants (2%), 2438 Black participants (27%), 1895 Hispanic participants (21%), 1065 participants of other race (12%), and 5233 White participants (59%). A total of 225 participants (3%) died during the study period, with a mean (SD) age at death of 27.7 (5.9) years. Incarceration in an adult correctional facility before the age of 18 years was associated with an increased risk of earlier mortality between 18 and 39 years of age compared with individuals who were never arrested or incarcerated before the age of 18 years (time ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.47-0.95). Being arrested before the age of 18 years was associated with an increased risk of earlier mortality between 18 and 39 years of age when compared with individuals who were never arrested or incarcerated before the age of 18 years (time ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.93).
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study of 8951 youths, the survival model suggested that being incarcerated in an adult correctional facility may be associated with an increased risk of early mortality between 18 and 39 years of age.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Confining Children in Adult Prisons and Premature Mortality-New Evidence to Inform Policy Action.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2321755. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.21755. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37405776 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Association of Incarceration With Mortality by Race From a National Longitudinal Cohort Study.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2133083. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33083. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34940867 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and Cause of Death Among Youths Previously Incarcerated in the Juvenile Legal System.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2140352. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.40352. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34940865 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile incarceration in an adult correctional facility as a risk factor for adolescent childrearing?J Adolesc. 2023 Jan;95(1):56-69. doi: 10.1002/jad.12096. Epub 2022 Oct 5. J Adolesc. 2023. PMID: 36199241
-
Opioid-related treatment, interventions, and outcomes among incarcerated persons: A systematic review.PLoS Med. 2019 Dec 31;16(12):e1003002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003002. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 31891578 Free PMC article.
-
Health status of detained and incarcerated youths. Council on Scientific Affairs.JAMA. 1990 Feb 16;263(7):987-91. JAMA. 1990. PMID: 2405202 Review.
Cited by
-
"It's easier to take a pill than fix a problem:" qualitative analysis of barriers and facilitators to antimicrobial stewardship program implementation in carceral settings.BMC Glob Public Health. 2024 Aug 26;2(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s44263-024-00090-1. BMC Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39681969 Free PMC article.
-
Hospital care while incarcerated: A tale of two policies.J Hosp Med. 2024 Mar;19(3):230-234. doi: 10.1002/jhm.13223. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Hosp Med. 2024. PMID: 37842851 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Error in Wording.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2326692. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.26692. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37486636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Criminal Justice Reform Is Health Care Reform.JAMA. 2024 Jan 2;331(1):21-22. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.25005. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38095916 Free PMC article.
-
Confining Children in Adult Prisons and Premature Mortality-New Evidence to Inform Policy Action.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2321755. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.21755. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37405776 Free PMC article. No abstract available.

